Figure 4.
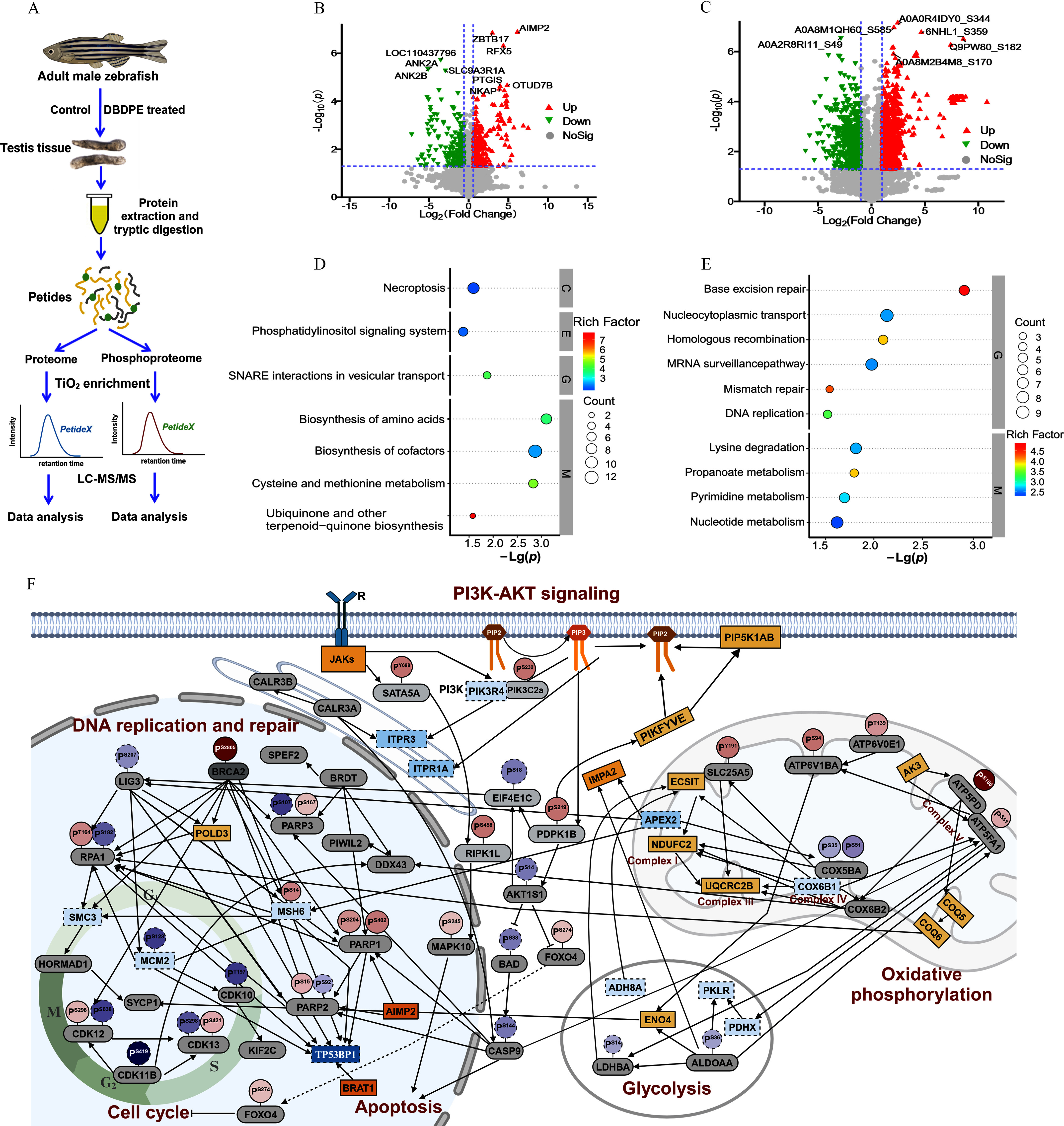
Whole-proteome and phosphoproteome analysis of male zebrafish testes after in vivo exposure to DBDPE. (A) Schematic diagram of proteome and phosphoproteome analysis. The illustration was in part created in BioRender (2024) https://BioRender.com/x32w463. (B) Volcano plot of quantified proteins in DBDPE-treated zebrafish testes. (C) Volcano plot of quantified phosphosites in DBDPE-treated zebrafish testes. Upward triangle (filled in red; on the upper right corner) and upside-down triangle (filled in green; on the upper left corner) in (B) and (C) indicate up-regulation and down-regulation, respectively; gray dots indicate no significant difference. (D) Significantly enriched KEGG pathways of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) from whole-proteome data. (E) Significantly enriched KEGG pathways of proteins harboring differentially phosphorylated sites from phosphoproteome data. The size of the dots in (D) and (E) represents the number of DEPs in the pathway, and the color of the dots represents the enrichment factors of KEGG pathway. (F) Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network after exposure to DBDPE. The illustration was created in BioRender (2023) https://BioRender.com/o93k219. Each large oval represents protein expression level, and smaller ovals with a tail on top represent phosphorylation levels of specific phosphorylation sites of the protein. Solid line boxes and dotted line boxes respectively indicate up-regulation and down-regulation in the proteome; gray-filled ovals indicate proteins without significant differences. Solid line circles and dotted line circles respectively indicate up-regulation and down-regulation in the phosphoproteome. Color intensity is proportional to (fold change). Data are reported in Excel Table S4. Note: DBDPE, decabromodiphenyl ethane; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; PI3K-AKT, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B; SNARE, soluble -ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor; , titanium dioxide.
