Figure 8.
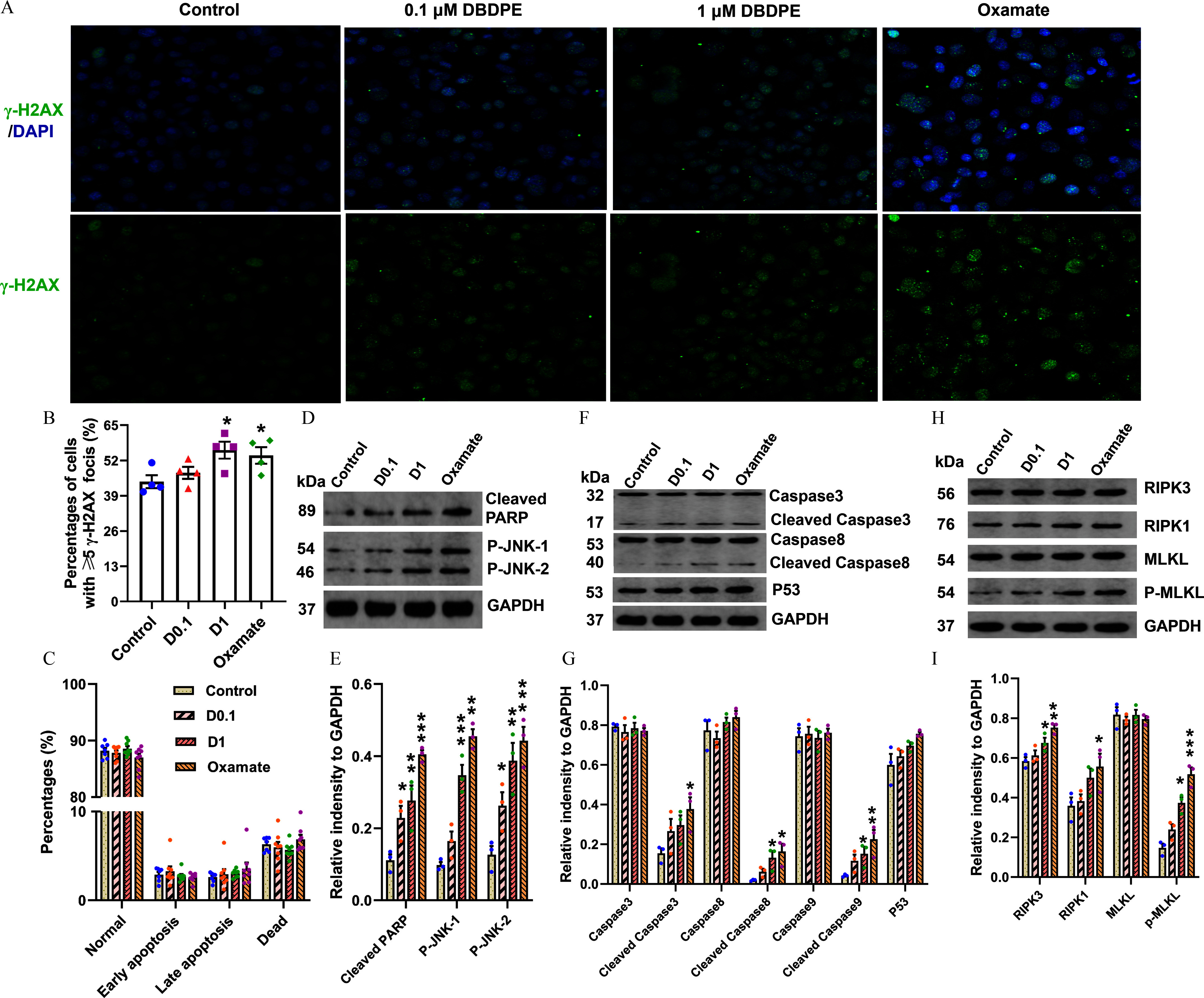
DNA damage and expression of proteins related to apoptosis or necroptosis in mouse spermatogonial GC-1 cells exposed to DBDPE and oxamate (LDH inhibitor) in vitro. (A) DNA damage in zebrafish testes detection by immunofluorescence staining against the histone protein -H2AX. The representative images show DAPI-stained (blue) nuclei with nuclear -H2AX foci in green. (B) Percentages of GC-1 cells with -H2AX foci (). (C) Cell apoptosis detection by flow cytometry (FCM) using an Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit (). (D) Western blotting analyses carried out with antibodies against caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, caspase-8, cleaved caspase-8, P53, and GAPDH in GC-1 cells. (E) Western blotting analyses carried out with antibodies against cleaved PARP, p-JNK, and GAPDH in GC-1 cells. (F) Western blotting analyses carried out with antibodies against RIPK3, RIPK1, MLKL, p-MLKL, and GAPDH in GC-1 cells. (H–I) Quantification of the abundances of proteins relative to GAPDH (). Each dot in (E–I) represents one replicate data point (one well of cells/replicate). The dot numbers represent the data size for statistical analysis. Results are represented as errors of the mean (SEMs). Data are reported in Excel Table S8. Note: DBDPE, decabromodiphenyl ethane; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like; PARP, poly(adenosine diphosphosphate-ribose) polymerase; p-JNK, phospho-c-jun N-terminal kinase; RIPK, receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 3. *, **, and *** indicate significant differences between exposure and control groups, by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the post hoc least significant difference (LSD) test.
