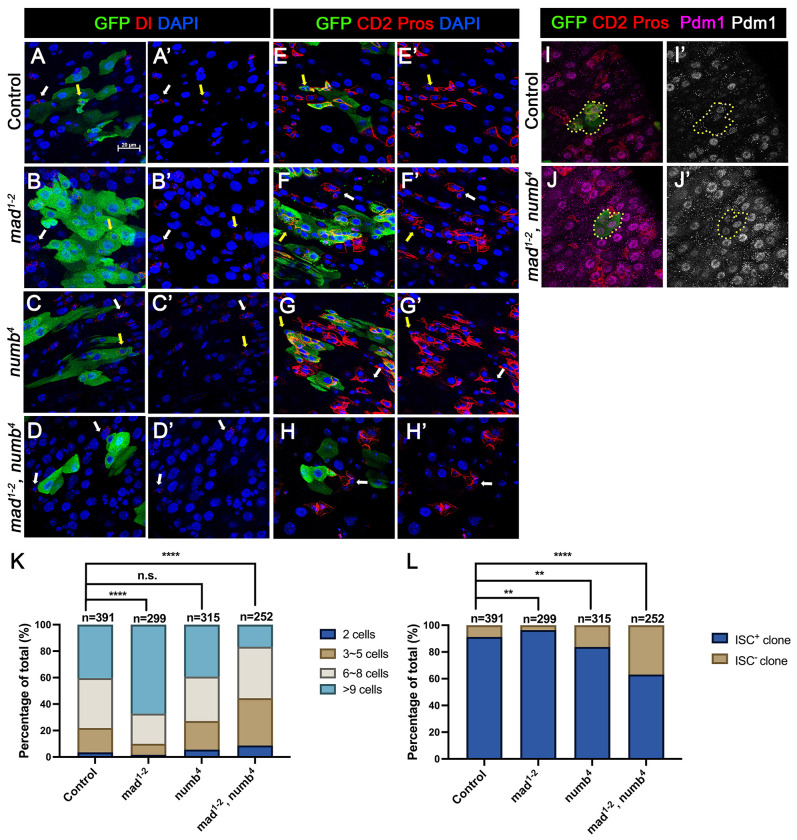
Figure 3. Loss of ISC in Numb and Mad depleted guts is due to ISC-to-EB differentiation.
(A-H’) Representative images of adult midguts containing MARCM clones (green) of FRT40 (Control) (A, A’, E, E’), mad1-2 (B, B’, F, F’), numb4 (C, C’, G, G’) and mad1-2, numb4 (D, D’, H, H’) and immunostained for GFP (green) and Dl (red and grey in A-D’) or E(spl)mβ-CD2 and Pros (red in A-D’ and grey in E-H’) at 14 days (grown at 18°C) after clone induction. GFP marks the clones. DAPI (blue) staining indicates nuclei. ISCs inside and outside the clones are indicated by yellow and white arrows, respectively.
(I) Representative images of adult midguts containing MARCM clones (green) of control (I, I’) or mad1-2, numb4 (J, J’) immunostained for GFP (green), E(spl)mβ-CD2 and Pros (red), and Pdm1 (magenta and grey). Scale bar (20 μm ) is presented in (A).
(K) Quantification of clone size for the indicated genotypes 14 days after clone induction.
(L) Quantification of numbers of clones with or without ISCs. Data are mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **, p < 0.01, ****, p < 0.0001.