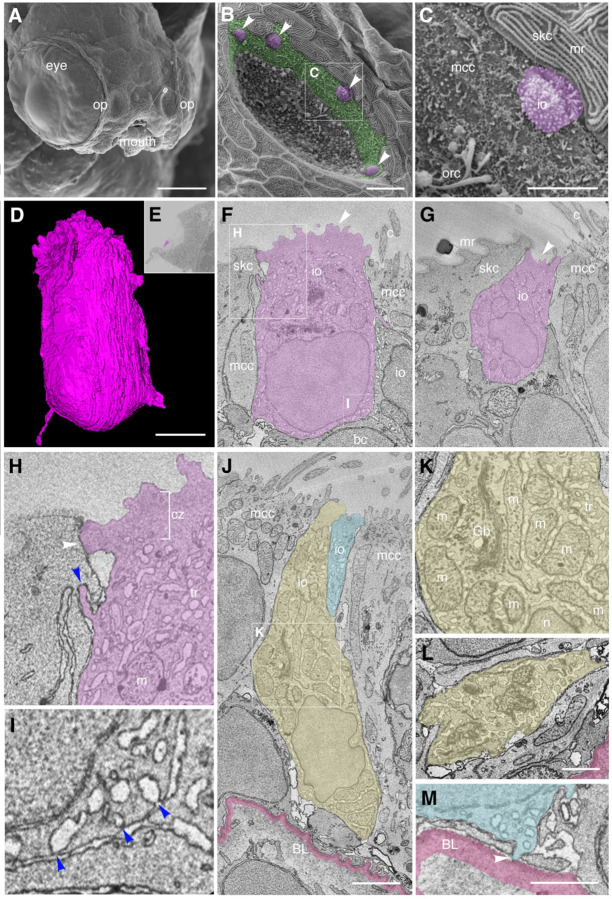
Figure 7. Ultrastructure and 3D reconstruction of NCC-like olfactory ionocytes in the non-sensory multiciliated cell zone of the zebrafish olfactory pit.
(A–C) Scanning electron micrographs of an ift88−/− zebrafish mutant embryo at 4 dpf. (A) Whole head showing location of the two olfactory pits (op). (B) Enlargement of the left-hand olfactory pit, boxed in A. The rounded apical surfaces of four ionocytes (presumed NCC-like) are highlighted in magenta (arrowheads). The peripheral zone of non-sensory multiciliated cells (mcc) is highlighted in green. (All olfactory cilia are missing in the ift88−/− mutant, allowing visualization of the apical surface of cells in the pit.) (C) Enlargement of the boxed region in B. An ionocyte (magenta) sits in the MCC zone, in contact with a skin cell with microridges (top right). The rods of two or three olfactory rod cells are also visible (bottom left; see also Fig. 3I in [80]).
(D–M) Ultrastructure and 3D reconstruction of ionocytes in the non-sensory multiciliated zone of the olfactory pit in a wild-type zebrafish larva at 7 dpf. (D) 3D reconstruction of a presumed NCC-like ionocyte, showing the microvillous apical surface. (E) Location of the ionocyte in D (magenta; arrowhead) at the lateral edge of the left olfactory pit. Coronal section. (F,G) Selected sections through the ionocyte shown in D, highlighted in magenta. The ionocyte makes contact with at least four other cell types: apically, with a skin cell on one side and a multiciliated cell on the other; basolaterally, with multiciliated cells, a basal cell, and another ionocyte. The microvillous apical surface is rounded in one area (F, arrowhead) but also forms a pit-like structure (G, arrowhead) in the same cell. (H) Enlargement of the boxed region in F (top left), highlighting tight junctional contact (white arrowhead) and interdigitation (blue arrowhead) between the ionocyte and a neighbouring skin cell. (I) Enlargement of the boxed region in F (bottom right), showing that pores where the tubular reticulum meets the plasma membrane are covered by a thin electron-dense structure (blue arrowheads). (J) Two examples of more elongated ionocytes highlighted in yellow and blue, with their apices sitting between multiciliated cells. (K) Enlargement of the boxed region in J, showing mitochondria-rich cytoplasm, Golgi apparatus and extensive tubular reticulum. (L) Section through the base of the yellow cell in J, showing the tubular reticulum. (M) An end-foot (arrowhead) of the blue ionocyte in J makes direct contact with the basal lamina (pink).
Abbreviations: bc, basal cell; BL, basal lamina (pink); c, cilia of multiciliated cell; cz, cortical zone (free of mitochondria; bracketed in H); Gb, Golgi body; io, presumed NCC-like ionocyte; m, mitochondrion; mcc, multiciliated cell; mr, microridges on skin cell; n, cell nucleus; op, olfactory pit; orc, olfactory rod cell (apical rods visible); skc, skin cell; tr, tubular reticulum.
Scale bars: A, 100 μm; B, 10 μm; C, 5 μm; D, 2 μm (applies to F, G); J; 2 μm; L, 1 μm; M, 1 μm.