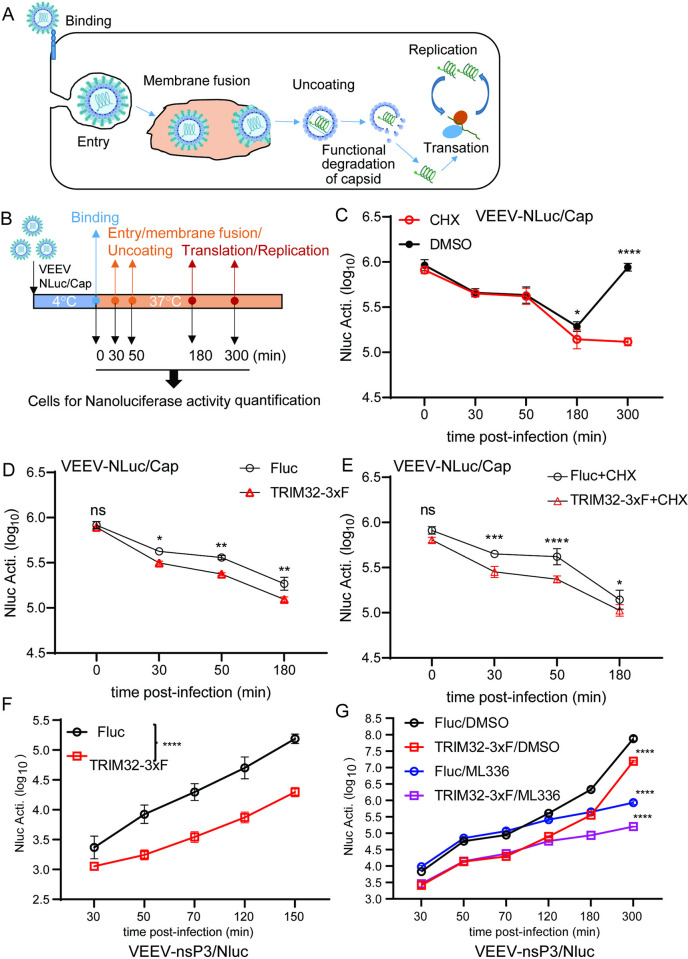
Fig 6. TRIM32 impairs the translation of incoming viral genome.
A. Schematic of the life cycle of VEEV. B. Schematic illustration of stability assay of VEEV nucleocapsids by using VEEV-NLuc/Cap infection. C. HeLa cells were infected VEEV-NLuc/Cap at 4°C for 1.5h, then the cells were washed and collected at the indicated time post temperature shift. D. HeLa-Fluc or HeLa-TRIM32 cells were infected with VEEV-NLuc/Cap at 4°C for 1.5h, then the cells were washed and collected at the indicated time post temperature shift. E. HeLa-Fluc or HeLa-TRIM32 cells were infected VEEV-NLuc/Cap at 4°C for 1.5h, then the cells were washed and collected at the indicated time post temperature shift in the presence or absence of CHX (75 ug/mL). F. HeLa-Fluc or HeLa-TRIM32 cells were infected with 1 MOI of VEEV-nsp3/NLuc at 37C for 20min, then the cells were washed and replaced with fresh media. The cells were collected at the indicated time points post infection, and the Nanoluciferase activity was measured. G. HeLa-Fluc or HeLa-TRIM32 cells were infected with 1 MOI of VEEV-nsp3/NLuc at 37°C for 20min, then the cells were washed and replaced with fresh media containing DMSO or 1μM ML336. The cells were collected at the indicated time points post infection, and the Nanoluciferase activity was measured. Data represent averages of independent biological replicates and are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined by 2-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001****P<0.0001). In C to G, the statistical significance was compared between Fluc and TRIM32-3xF-expressing cells at each time point.