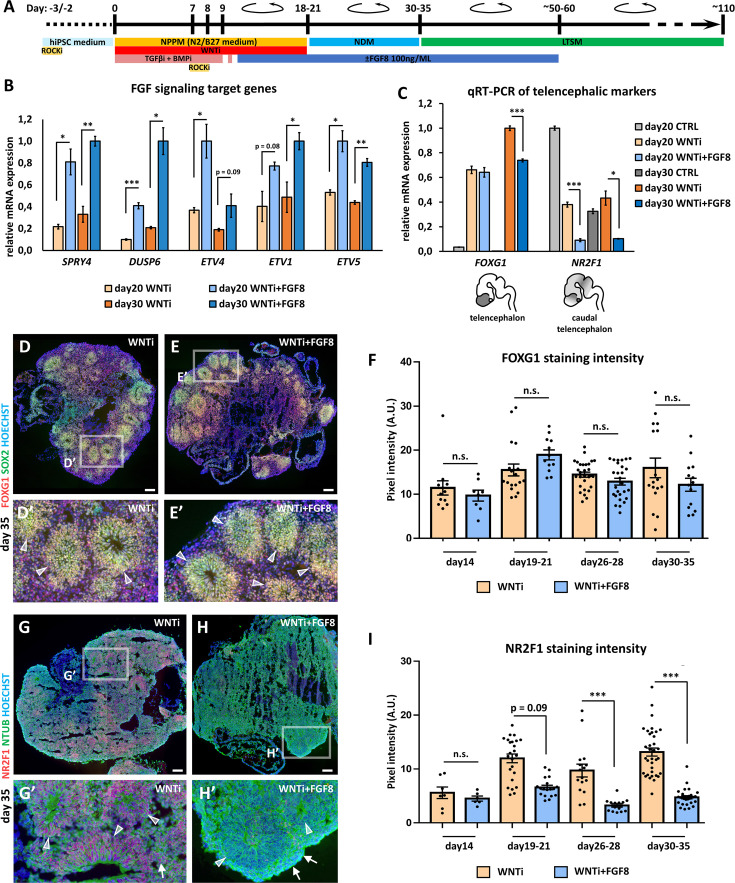
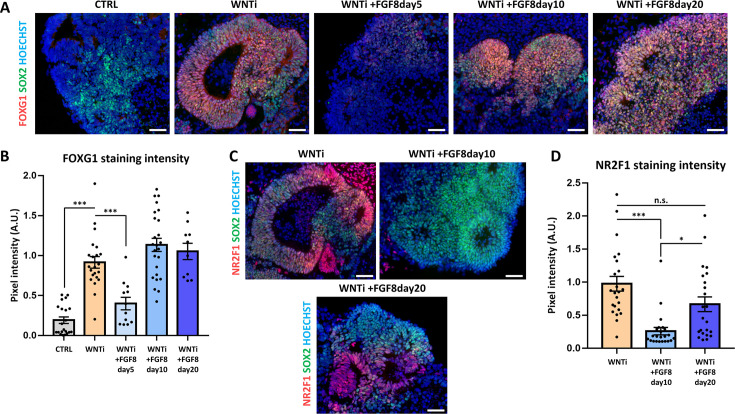
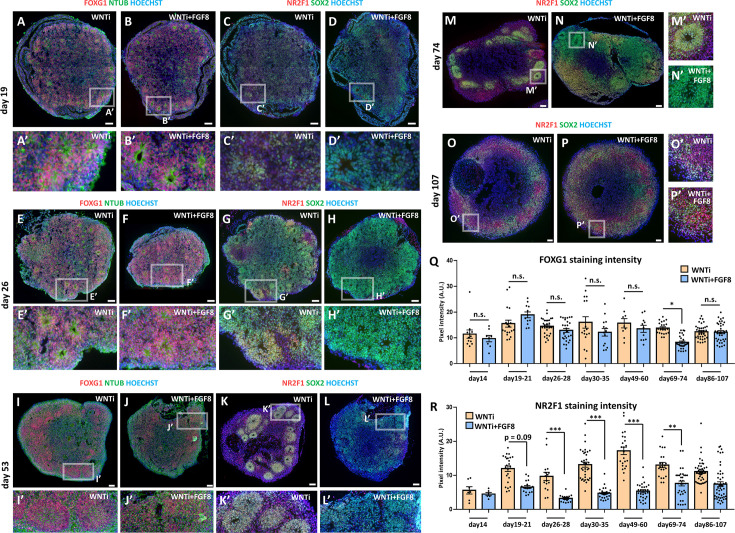
Figure 2. FGF8-mediated regulation of target gene expression in FOXG1+ telencephalic organoids.
(A) Schematic of the hybrid 2D/3D method for applying FGF8 treatment on telencephalic/cortical human organoids in vitro. FGF8 (100 ng/mL) was added to the neural progenitor patterning medium (NPPM) beginning on day10-11 (blue bar) and maintained through subsequent culture steps until approximately day50-60. (B) Real-time qRT-PCR analysis of FGF8 target gene expression (SPRY4, DUSP6, ETV4, ETV1, and ETV5) in day20 and day30 organoids treated with WNT inhibition alone (WNTi) or in combination with FGF8 (WNTi + FGF8), as indicated. n=3 organoids per condition, pooled prior RNA extraction. (C) Real-time qRT-PCR quantification of FOXG1 (telencephalic marker) and NR2F1 (caudal telencephalic marker and FGF8 target) expression in day20 and day30 control (CTRL), WNT-inhibited (WNTi), and FGF8-treated (WNTi + FGF8) samples, as indicated. FGF8 treatment effectively downregulates NR2F1 expression in WNTi + FGF8 organoids compared with WNTi organoids. n=3 organoids per condition, pooled prior RNA extraction. (D–F) Immunostaining for FOXG1 (red) and SOX2 (green) in day35 WNTi and WNTi + FGF8 organoids, as indicated. FGF8 treatment does not significantly alter FOXG1 expression. White arrowheads in high-magnification images indicate SOX2+ NR2 F1+ NPs within rosettes. Graph (F) shows pixel intensity quantification of FOXG1 staining in WNTi and WNTi + FGF8 organoids at different time points. n≥8 sections from n≥4 organoids from n≥2 distinct batches. (G–I) NR2F1 and NTUB (red and green, respectively, in G-H’) immunostainings on day35 WNTi and WNTi + FGF8 organoids, as indicated. FGF8 treatment efficiently modulates NR2F1 expression (compare G and H). High-magnification images (G’ and H’) show neural rosettes (NTUBlow, indicated by white arrowheads) and differentiating neurons (NTUBhigh, indicated by white arrows), both expressing NR2F1 (red) in WNTi organoids, but lacking NR2F1 in WNTi + FGF8 organoids. Graph (I) displays pixel intensity quantification of NR2F1 staining in WNTi and WNTi + FGF8 organoids over time. n≥6 sections from n≥4 organoids from n≥2 distinct batches. Scale bars: 100 µm.