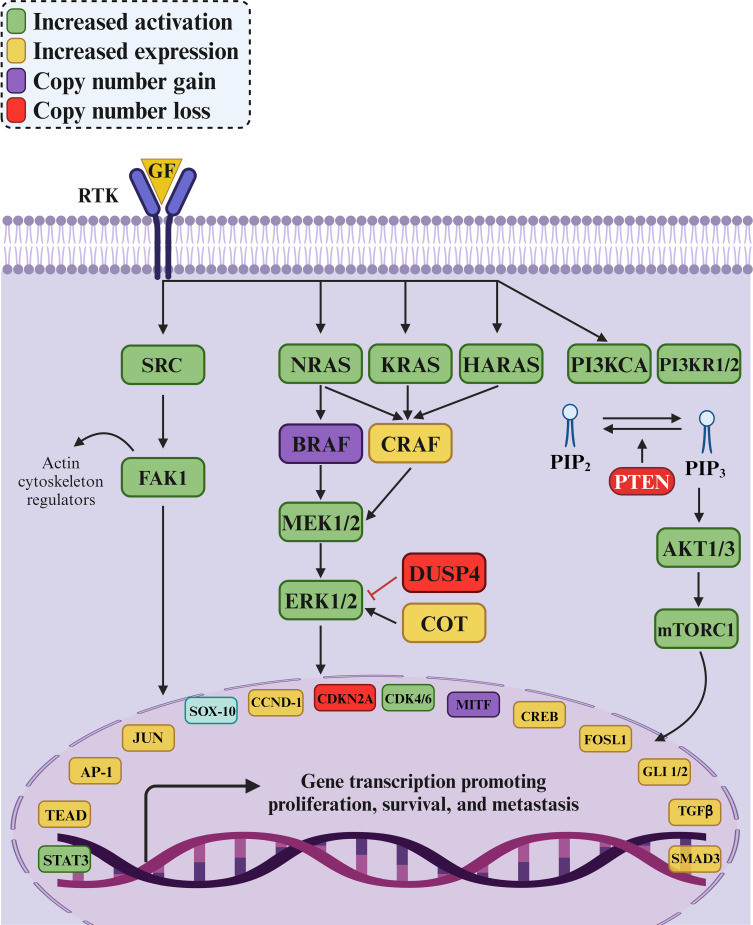
Figure 5.
The MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and its role in cancer development. The pathway governs cell proliferation, survival, and metastasis through interactions among key proteins and enzymes like SRC, KRAS, BRAF, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2. Increased activation (green) and expression (yellow) of pathway components often lead to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer progression. Mutations, such as KRAS mutations in colorectal cancer and BRAFV600E mutations in melanoma and colorectal cancer, hyperactivate the pathway, promoting tumorigenesis and metastasis. Loss of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN (red) activates the PI3K/AKT pathway, contributing to cancer progression by enhancing cell proliferation and survival. DUSP4, a negative regulator of ERK1/2, may experience copy number loss, diminishing its ability to control pathway activity. The intricate nature of the MAPK/ERK pathway and its crosstalk with other signaling pathways highlight the importance of targeted therapies to disrupt these interactions and effectively combat cancer.