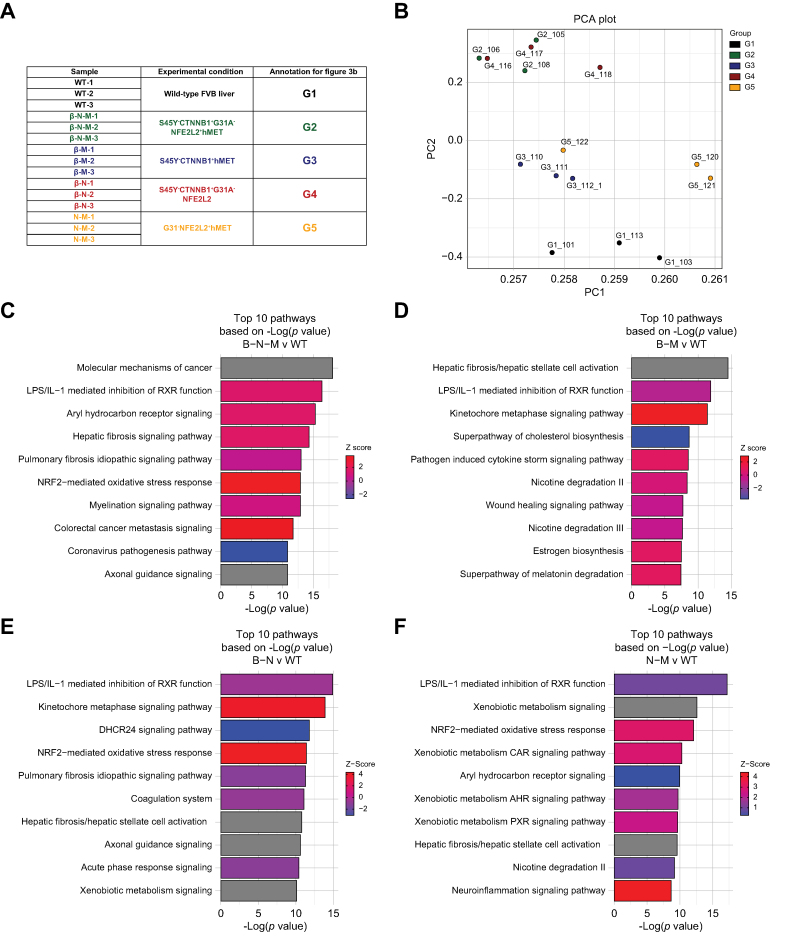
Fig. 3.
Transcriptomic analysis of multiple β-catenin-mutated and non-mutated models reveals differences in gene expression.
(A) Description of the samples used for transcriptomic analysis. Each mouse tumor model had three replicates sequenced. (B) Principal component analysis demonstrates clustering of wild-type distinct from the tumor models, with models of high Met activity clustering similarly and models of high Nrf2 activity clustering similarly. (C) Top 10 pathways based on p value from ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) of differentially expressed genes comparing S45Y-CTNNB1-G31A-NFE2L2-hMET to wild-type. Specifically, 4,577 differentially expressed genes were applied to IPA analysis with cutoff of false discovery rate (FDR) = 0.05 and absolute log fold change >1.5. (D) Top 10 pathways based on p value from IPA of differentially expressed genes comparing S45Y-CTNNB1-hMET to wild-type. Specifically, 1,543 differentially expressed genes were applied to IPA analysis with cutoff of FDR = 0.05 and absolute log fold change >1.5. (E) Top 10 pathways based on p value from IPA of differentially expressed genes comparing S45Y-CTNNB1-G31A-NFE2L2 to wild-type. Specifically, 4,355 differentially expressed genes were applied to IPA analysis with cutoff of FDR = 0.05 and absolute log fold change >1.5. (F) Top 10 pathways based on p value from IPA of differentially expressed genes comparing G31A-NFE2L2-hMET to wild-type. Specifically, 1,864 differentially expressed genes were applied to IPA analysis with cutoff of FDR = 0.05 and absolute log fold change >1.5. For (C–F) ranking of pathways based on -log(p value) and activation/inhibition of pathway determined by z-score.