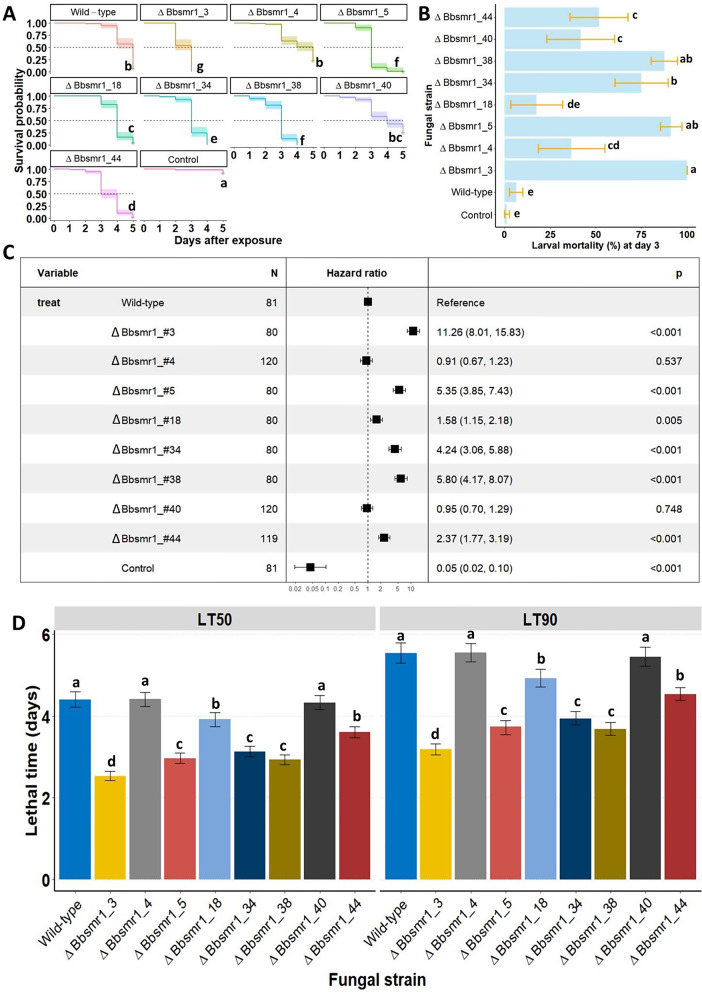
Fig. 3.
Knockout Bbsmr1 mutants of B. bassiana exhibit varied degrees of virulence against the greater wax moth. A) Single-dose survival response of Galleria mellonella larvae following exposure to eight different mutant strains (designed ΔBbsmr1). Inoculum concentration at 1 × 107 blastospores/mL and insects were treated using the direct contact application by exposing larvae for 10 s to 1 mL of blastospore suspension. Natural mortality in controls were attributed to unknown causes with dead larvae appearing all black and putrefied. Survival curves were compared with non-parametric log-rank test and lettering indicates significant differences (P < 0.05). B) Overall mortality confirmed by mycosis of G. mellonella after 3 days post-treatment with blastospores of ΔBbsmr1 and wild-type strains. Means (± SE) not sharing any letter are significantly different by Tukey’s HSD (P < 0.05). C) Vertical bars represent median and 90% lethal times estimated by Weibull parametric model fitted to survival data followed by their respective 95% confidence intervals. Lettering indicates significant differences based on the non-overlapping of confidence intervals. D) Hazard ratio depicting the likelihood of insect death occurring after exposure to B. bassiana mutants in relation to the wild-type. The higher this ratio the greater the risk of death imposed by the mutant strain in comparison to the wild-type. P values are given for all comparisons