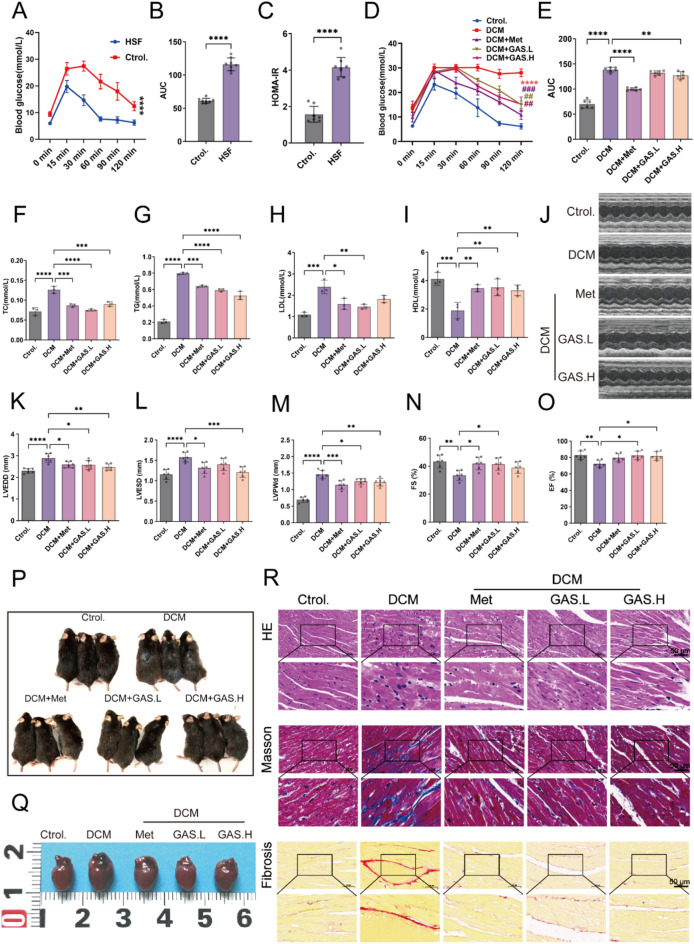
Fig. 1.
Impaired cardiac function and myocardial pathological changes in DCM mice were ameliorated by GAS. After one week of acclimation, the mice were fed an HSF diet for eight weeks, whereas the control group received a normal diet. A Fasting blood glucose levels in the mice. B Area under the curve of blood glucose decline. C Insulin sensitivity in mice. After insulin resistance occurred, the HFS group was administered intraperitoneal injections of STZ (30 mg/kg/day) three times a day for two days. The normal control group was injected with an equal volume of saline. After DCM was established in the mice, D–R was administered by gavage once every two days for 12 weeks. D Fasting blood glucose levels in DCM mice; * P < 0.05 vs. control; # P < 0.05 vs. DCM. E Area under the curve of blood glucose decline. F–I. Lipid quadruple content TC, TG, LDL, and HDL assays. J–O Small-animal ultrasonography was performed to detect the parameters of left ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic internal diameters (LVEDD and LVESD), left ventricular posterior wall thickness at end-diastole (LVPWd), fractional shortening (FS), and ejection fraction (EF) (n = 6). P–Q Degloving phenomenon and heart size in mice. R H&E staining, Masson staining, and Sirius Red staining (n = 3). The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of three or more independent experiments; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001.