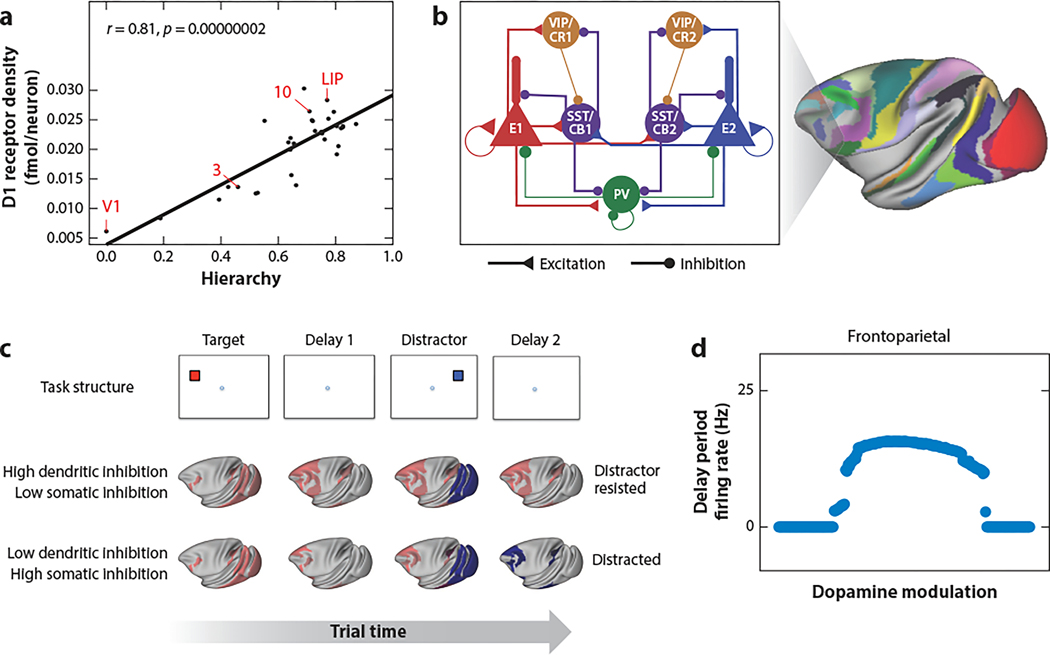
Figure 5.
Dopamine modulation of a multiregional cortical system. (a) The D1 receptor density per neuron increases along the anatomically defined cortical hierarchy. (b) An extended local circuit model with diverse types of inhibitory neurons. (c) Simulations of a working memory task with a distractor. With a high dendritic-somatic inhibition ratio (top row), target-selective activity (red) is maintained in the second delay in spite of the distractor that briefly causes activity in the distractor-selective neural population (blue) of visual cortical areas (middle row). With a low dendritic-somatic inhibition ratio, persistent activity becomes selective for the distractor in the second delay (bottom row). (d) Inverted U-shaped dependence on D1 modulation of persistent activity in the parietofrontal cortical areas. Abbreviations: 3, primary somatosensory cortex Brodmann area 3; 10, frontal polar cortex Brodmann area 10; E, excitatory neurons; LIP, lateral intraparietal cortex; PV, parvalbumin; SST/CB, somatostatin/calbindin; V1, primary visual cortex; VIP/CR, vasoactive intestinal peptide/calretinin-expressing inhibitory neuron. Figure adapted from Froudist-Walsh et al. (2021) (CC BY 4.0).