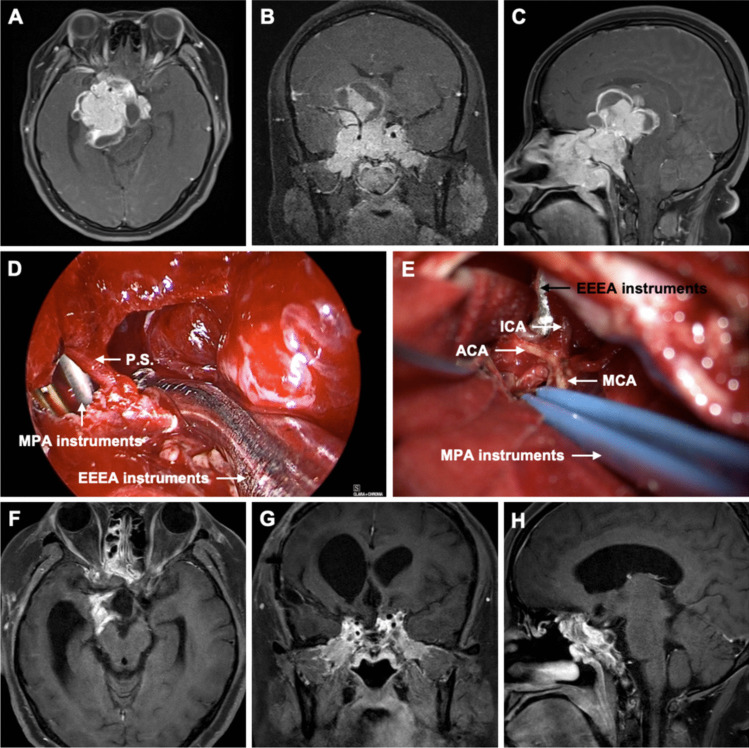
Fig. 2.
Preoperative axial (A), coronal (B), and sagittal (C) gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MR images showed an irregular mass in the middle cranial fossa measuring 7.3 × 5.9 × 5.8 cm. Superiorly, it protruded into the suprasellar cistern. Laterally, it invaded the bilateral cavernous sinuses, encasing the C2-C7 segments of the bilateral internal carotid arteries and the M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery. Anteriorly, it invaded the bilateral optic canals, superior orbital fissure, ethmoid sinus, sphenoid sinus, and nasopharynx. Posteriorly, it protruded into the interpeduncular cistern and pontine cistern, compressing the right pons and right cerebral peduncle. D Intraoperative image from the EEEA, showing the tumor debulking delivered through the transcranial route. E Intraoperative image from the MPA, showing the internal carotid artery (ICA), anterior cerebral artery (ACA), and middle cerebral artery (MCA). Postoperative axial (F), coronal (G), and sagittal (H) gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MR images obtained 3 months after surgery showed gross total resection (GTR) of the tumor. P.S.: pituitary stalk, EEEA: expanded endoscopic endonasal approach, MPA: microscopic pterional approach