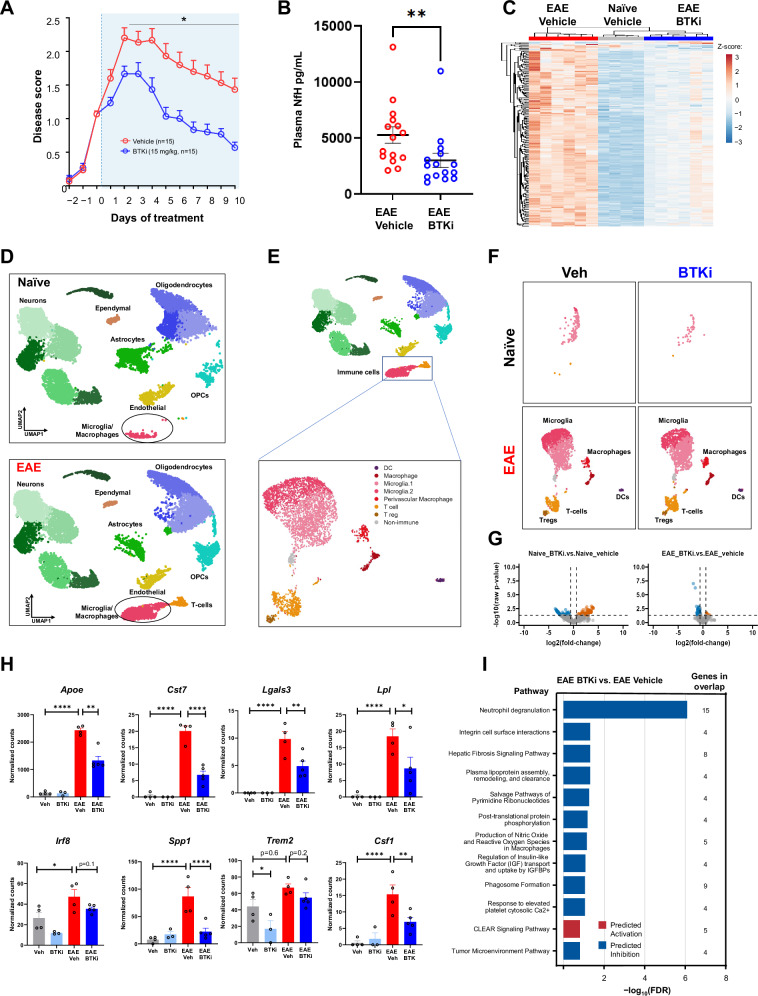
Fig. 1. BTK inhibition with PRN2675 in the C57BL/6 EAE mouse model of MS.
A Disease scores over time. Therapeutic treatment started once disease scores reached 1.0–1.5. B Plasma NfH concentrations at Day 10 (n = 15 mice. Shown p-value is 0.0032, calculated with a two-tailed Mann Whitney test). C Heatmap of PRN2675-dependent transcriptional signature genes. Heatmap displays DESeq2 normalized counts scaled using a Z-score. Spinal cord tissue was collected after 10 days of vehicle or PRN2675 treatment and bulk RNA-seq was performed. Differential expression analysis was performed using DESeq2. The PRN2675-dependent transcriptional signature consists of 253 genes with an absolute (fold-change) ≥1.5 and FDR ≤ 0.05 when comparing EAE + PRN2675 to EAE + vehicle. D UMAP representation of single-nuclei RNA sequencing analysis of 52,655 cells from EAE mouse spinal cords. Clusters were identified using Seurat and several known markers for each cell type. Spinal cord tissue was collected after 8 days of vehicle or PRN2675 treatment and single-nuclei RNA-sequencing was performed. E UMAP of immune cell-type subclusters identified by sub-clustering analysis of microglia/macrophage and T-cell clusters shown in (D). F UMAP of immune cell-type clusters, as in (E), identified in naive and EAE animals, with or without PRN2675. G Pseudo-bulk analysis of microglia subclusters identified in (E) and volcano plots of differential gene expression between PRN2675-treated and untreated mouse spinal cord. Plots are shown for both naive and EAE mice. Differential expression analysis was performed using DESeq2 (absolute(fold-change) ≥1.5 and raw p-value ≤ 0.05). H DESeq2 normalized counts of disease-associated microglial genes, identified in (G). Shown p-values are unadjusted and were calculated using Wald significance test implemented in DESeq2 (n = 3–5 mice). P-values are available in the Source Data file. I Pathway analysis using IPA: EAE + PRN2675 vs EAE + vehicle. The 12 pathways that demonstrated the largest change (−log10(FDR)) and showed direction (i.e., had a z-score available) are presented. All 12 pathways shown were downregulated with EAE + PRN2675 vs EAE+ vehicle. The pathway analysis gene list is the PRN2675-dependent transcriptional signature identified in the right plot of panel G. P-values are indicated by * ≤ 0.05, ** ≤ 0.01, *** ≤ 0.001, and **** ≤ 0.0001. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.