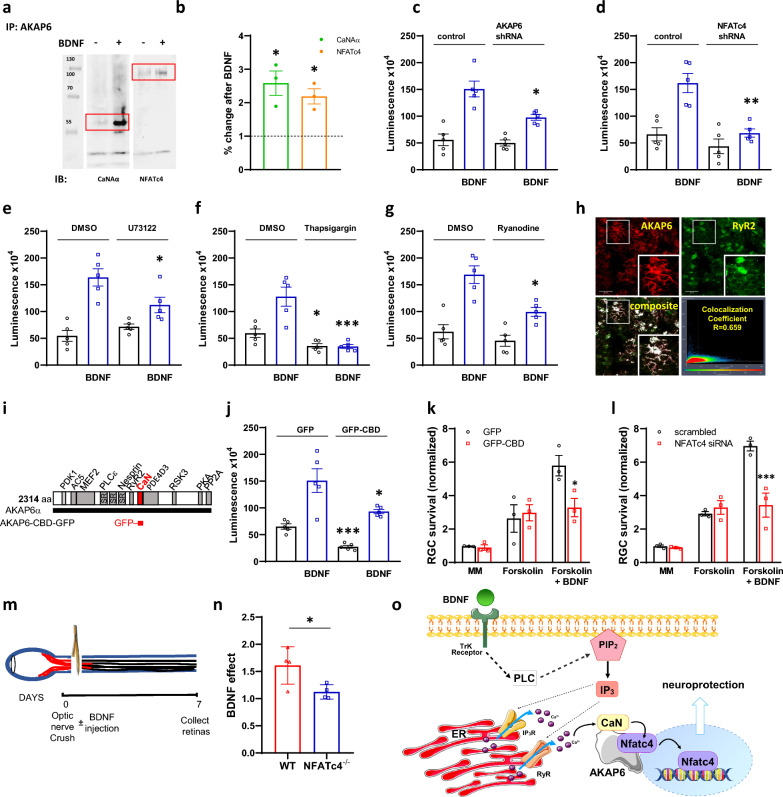
Fig. 1.
AKAP6 regulates NFAT activity for BDNF-mediated neuronal survival. A The AKAP6 antibody was used for immunoprecipitation of endogenous calcineurin (catalytic Aα subunit, CaN) or NFATc4 proteins from primary hippocampal neurons following incubation with BDNF. All presented blots are representative of experiments conducted at least three times. B Quantitative densitometric analysis of band intensity. The results are expressed in arbitrary units, defined as the optical density per milligram of protein relative to vehicle-treated cells, which were set as 100%, n = 3. C Primary hippocampal neurons were co-transduced with NFAT dual-reporter lentivirus and Lenti-AKAP6 shRNA (or an appropriate control), or alternatively, with D Lenti-NFATc4 shRNA (or an appropriate control). NFAT transcriptional activity was assessed in cell lysates following BDNF stimulation by quantifying luciferase activity (n = 5). E Hippocampal neurons were pretreated with 1 μM PLC inhibitor—U73122 or F 1 μM sarco(endo)plasmic Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor—thapsigargin or G 20 μM ryanodine receptor inhibitor—ryanodine (n = 5 for each) and luciferase activity was quantified 12 h following BDNF stimulation. H Colocalization of AKAP6 and ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) in primary hippocampal neurons. Fixed cells were immunostained with anti-AKAP6 primary and respective Alexa Fluor 594 conjugated secondary antibody (shown in red), as well as with anti-RyR2 primary antibody and respective Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated secondary antibody (shown in green). Colocalization percentage (fraction of AKAP6-positive pixels which are also positive for RyR2) was calculated using Leica LAS AF Lite software. Scale bars: 20 μM. I The design of CaN anchoring disruptor. The sequence corresponding to AKAP6 CaN binding domain (aa 1286–1345, CBD) was subcloned into rAAV-CAG-EGFPSV40 vector for AAV2 production. J Hippocampal neurons were co-transduced with NFAT dual-reporter lentivirus and AAV2-CBD-GFP (or AAV2-GFP control) for assessment of NFAT transcriptional activity (n = 5). K In vitro survival of RGC transduced with AAV2-CBD-GFP or AAV2-GFP alone, or L electroporated with NFATc4 or control siRNA and cultured in media with or without BDNF, normalized to appropriate control-treated RGCs cultured in minimal media (no forskolin, no BDNF). Representative data from repeated experiments shown (n = 3). M Experimental design of the optic nerve crush (ONC) in vivo model. BDNF was intravitreally injected immediately following ONC, and retinas were collected 7 days after. N Quantification of BDNF effect on RGC survival in vivo following ONC in wild-type (WT) or Nfatc4−/− mice. Retinal ganglion cells were stained with anti-RBPMS antibody and counted manually. Data are expressed as the ratio of RBPMS-positive cells in the BDNF-treated eye relative to control (PBS-injected) eye (n = 4 per group). The RGC densities (cells per mm2) in the Sham-operated groups are as follows: 3243 ± 89 for WT and 3159 ± 57 for Nfatc4−/− mice. O The schematic model of AKAP6-dependent regulation of NFAT transcriptional activity in response to BDNF stimulation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard error of mean (± SEM)