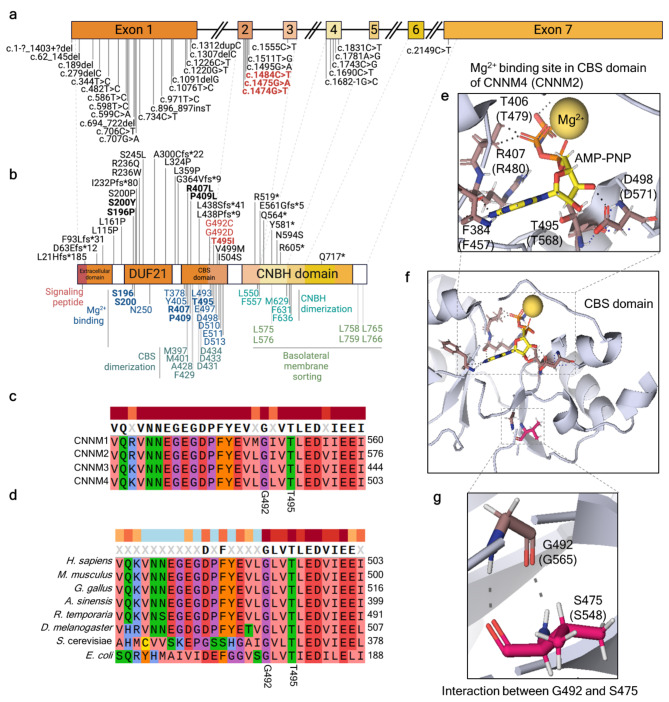
Fig. 1.
In silico functional prediction of p.(Gly492Cys), p.(Gly492Asp), and p.(Thr495Ile) variant in CNNM4 protein. (a) CNNM4, located on chromosome 2q11.2, consists of seven exons and six introns (created with BioRender.com). All reported pathogenic variants associated with Jalili syndrome (JS) are indicated, with the bold text highlighting the variants selected for functional characterization in this study. (b) Four key domains of the CNNM4 protein are illustrated from the N-terminal to C-terminal: the extracellular domain, domain of unknown function 21 (DUF21), cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) domain, and cyclic nucleotide-binding homology (CNBH) domain. The signal peptide is located at the N-terminal. The top panel displays amino acid alterations corresponding to reported JS variants, while the lower panel shows the functionally characterized residues based on 3D structural determination. Pathogenic variants from JS patients are indicated in bold text, with those included in this functional study highlighted in bold red text (created with BioRender.com). (c) Amino acid alignment within the CNNM protein family. (d) Amino acid sequence alignment of CNNM4 across various organisms. (e, f) Structure of the Mg2+−ATP binding site within the CBS domain. (g) Interaction between Gly492 and Ser475 in the CBS domain of CNNM4 is depicted, with corresponding residues from CNNM2 shown in parentheses. References are provided in Supplementary Tables S1-2.