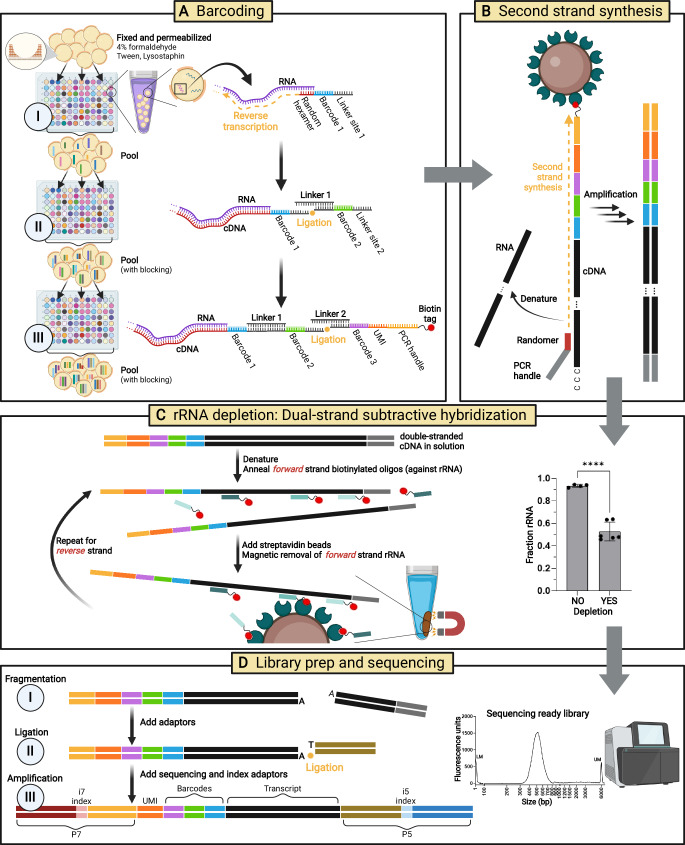
Fig. 1. BaSSSh-seq enables bacterial scRNA-seq of biofilm and incorporates rRNA depletion.
A Split-pool barcoding attaches a combination of three barcodes to intracellular RNA transcripts of fixed and permeabilized cells. The 5′ end of the terminal barcode oligo also includes a UMI, PCR handle, and biotin tag. B Following lysis, streptavidin magnetic beads are used to purify captured transcripts. Then double-stranded cDNA is synthesized via random primer second strand synthesis and PCR amplification. C Substantial rRNA depletion is performed using an enzyme-free dual-strand subtractive hybridization technique, where biotin-tagged oligos specific to 5S, 16S, and 23S rRNA fragments are annealed to each cDNA strand and magnetically removed with streptavidin beads. The rRNA content can be lowered from >90% to <50% (****, p-value < 0.0001 by unpaired t-test). Data includes 4 biological replicates with no depletion (25,000 cells per sample library, 1.5 × 105–2.5 × 105 paired-end reads per sample) and 6 biological replicates with depletion (120,000–150,000 cells per sample library, 2.4 × 107–4.4 × 107 paired-end reads per sample). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. D Libraries are constructed for Illumina sequencing through fragmentation, ligation, and amplification to generate constructs containing P5/P7 ends with unique i5/i7 index combinations. Schematic created in BioRender: Korshoj, L. (2024) BioRender.com/o39n335. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.