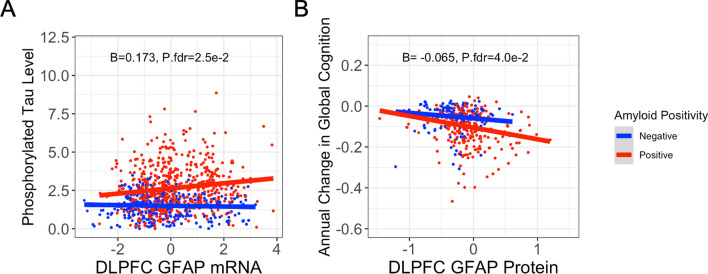
Fig. 4.
Significant interactions of GFAP expression and amyloid status. A High GFAP mRNA expression in the dlPFC relates to a high brain phosphorylated tau burden in amyloid-positive individuals. Phosphorylated tau was quantified by immunohistochemistry, and amyloid positivity was defined as CERAD “moderate” or “frequent.” Unadjusted scatter plots and statistical results from linear regression models adjusting for age at death, sex, and post-mortem interval. B High GFAP protein expression in the dlPFC relates to a faster rate of global cognitive decline in amyloid-positive individuals. Amyloid-positivity was defined as CERAD “moderate” or “frequent.” Unadjusted scatter plots and statistical results from linear mixed-effects regression models adjusting for age at death, sex, education, time from last study visit to death, and post-mortem interval. Time was represented as years from the final visit, with both time and intercept included as fixed and random effects