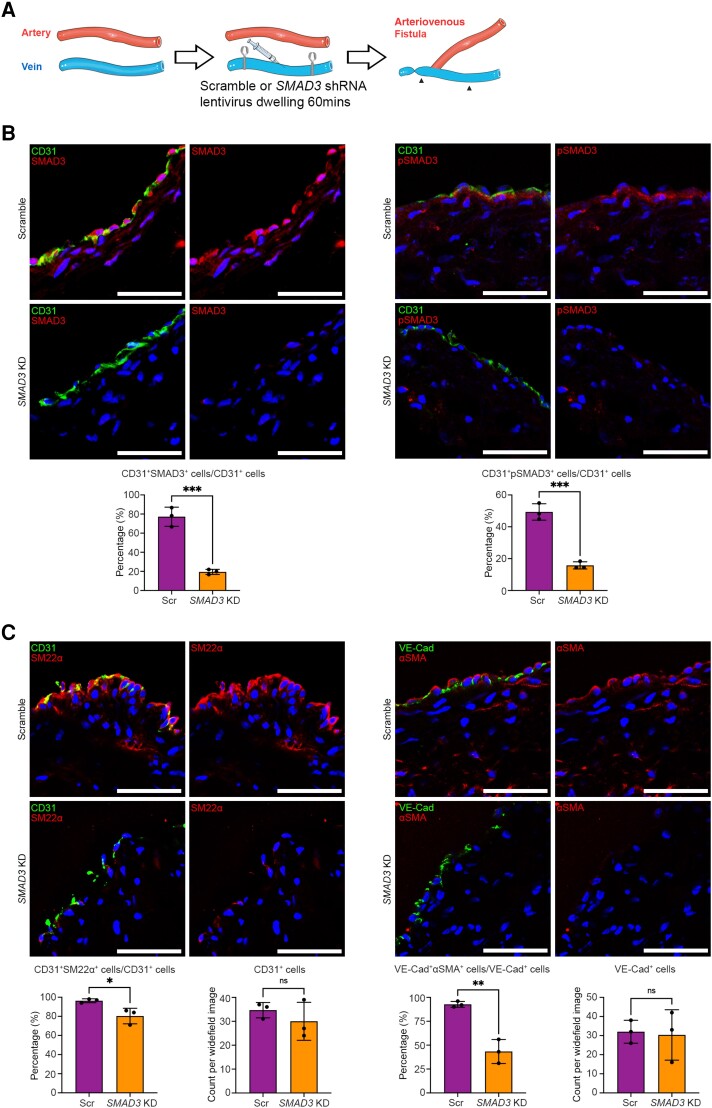
Figure 2.
Efficacy of SMAD3 knockdown and inhibition of EndMT in preclinical large animal AVF model (Phase 1). (A) Schematic representation of the surgical method including dwelling of lentivirus. Here, in Phase 1, the AVF in the right leg was harvested from six pigs 8 days after AVF creation, where three pigs were randomized to receive lentivirus carrying scramble shRNA (Scr; controls) and three pigs received lentivirus carrying SMAD3 shRNA (SMAD3 KD). Arrowheads indicate the section of vein where the lentivirus was allowed to dwell. (B) Representative immunofluorescence staining and quantitation of SMAD3 and pSMAD3 in endothelial cells 8 days after AVF creation. CD31 is shown in green, SMAD3 or pSMAD3 in red, and DAPI in blue. (C) Representative immunofluorescence staining and quantitation of EndMT and luminal endothelial cell coverage, 8 days after AVF creation. Endothelial markers (CD31 and VE-Cad) are shown in green. Mesenchymal markers (SM22α and αSMA) are in red. DAPI-stained nuclei are in blue. Analyses were performed using unpaired Student’s t-test. All scale bars = 50 µm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. n = 3 pigs per group for all analyses.