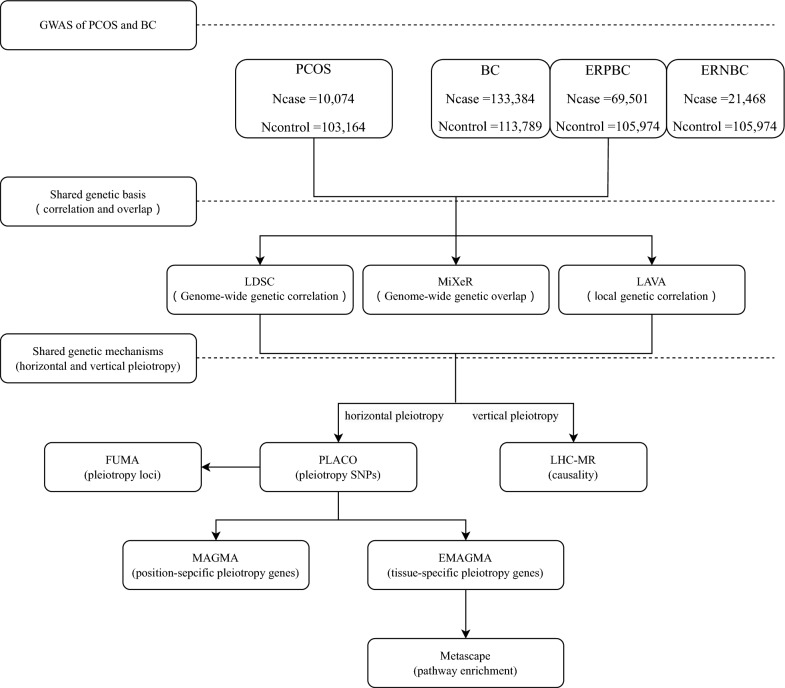
Fig. 1.
Study design. Summary statistics were retrieved from publicly available GWASs conducted for PCOS and BC. The genetic basis between the two diseases was explored through multiple analytical methods. Genome-wide genetic correlations were estimated using LDSC, while genome-wide genetic overlap was assessed through MiXeR. Additionally, local genetic correlations were examined using LAVA. Together, these analyses provide a comprehensive view of the shared genetic architecture between the two conditions. The shared genetic mechanism of the two diseases was analyzed, and the horizontal effect was studied at four levels. PLACO was employed to identify pleiotropic SNPs, which were subsequently annotated to genomic loci using FUMA. Location-specific pleiotropic genes were identified through MAGMA, while eMAGMA was used to uncover tissue-specific pleiotropic genes at the gene level. Lastly, Metascape was applied to perform functional enrichment analysis on the significant genes identified by eMAGMA, providing insights into the biological processes and pathways involved. We applied LHC-MR to evaluate the pairwise causal associations between PCOS and the BC, primarily elucidating the contributions from vertical pleiotropy