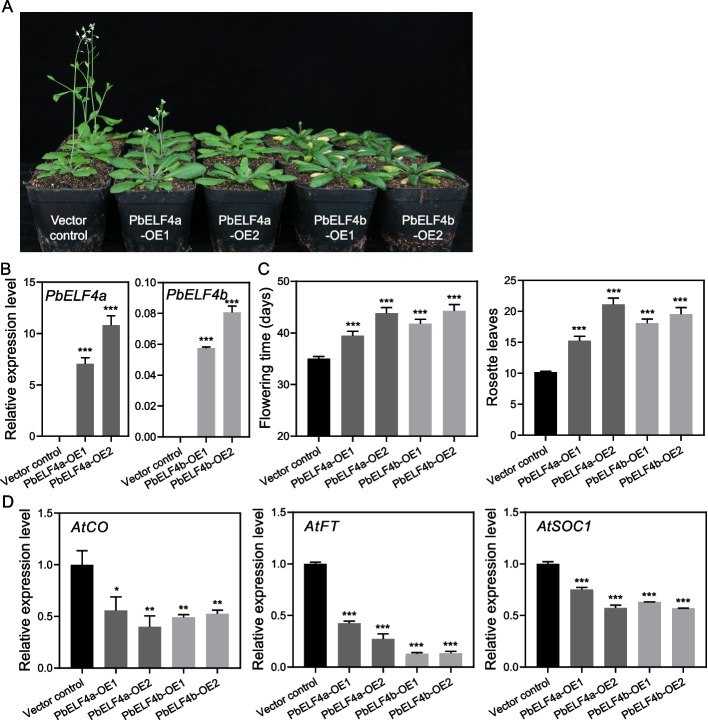
Fig. 4.
Overexpression of PbELF4a and PbELF4b delayed flowering in Arabidopsis plants. A Flowering phenotypes of vector control plants, PbELF4a-OE, and PbELF4b-OE transgenic lines grown under long-day conditions (16 h light/8 h dark) for 38 days. The number of rosette leaves of vector control plants was 10, while PbELF4a-OE1 lines was 13 and 14. The first flower of PbELF4a-OE2, PbELF4b-OE1, and PbELF4b-OE2 did not open; hence, the number of rosette leaves was not counted. B Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of PbELF4a and PbELF4b expression in control plants and transgenic lines. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). C Days to first flowering and number of rosette leaves at first flowering of control plants and transgenic lines. Data are presented as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (n ≥ 24). D Expression levels of flowering-related genes in 10-day-old seedlings from control plants and transgenic lines. The expression of each gene in control plants was normalized to a value of “1.” AtACT served as the internal control for gene expression analysis. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t-tests compared to the vector control plants. * Indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.01, and *** indicates P < 0.001