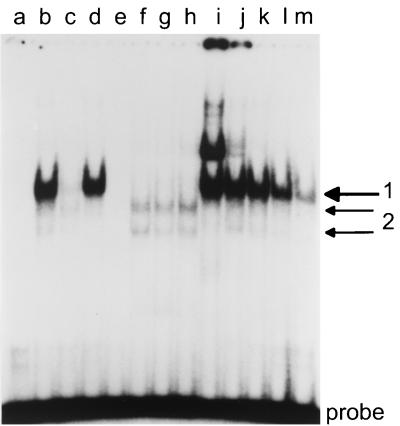
FIG. 6.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay: binding of nuclear proteins from Mutu I cells to the CBF1 site and to a mutant control oligonucleotide. Labeled double-stranded oligonucleotides containing a CBF1 consensus site and a mutant site disabled for CBF1 binding were incubated with 1 μg of crude nuclear extract from Mutu I cells with the oligonucleotides, amounts of poly(dI-dC), and unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides as indicated. The resulting protein-DNA complexes were separated in a 4% polyacrylamide gel. Lanes a to h and k, 1 μg of poly(dI-dC) added; lanes a to d and i to m, labeled CBF1 oligonucleotide as a probe; lanes e to h mutant oligonucleotide labeled as a probe. Lane 2, no protein added; lane b, nuclear extract; lane c, shift competed with a 50-fold excess of unlabeled CBF1 oligonucleotide; lane d, competition with a 50-fold excess of unlabeled mutant oligonucleotide; lane e, no protein added; lane f, nuclear extract; lane g, competition with a 50-fold excess of unlabeled CBF1 oligonucleotide; lane h, competition with a 50-fold excess of unlabeled mutant oligonucleotide; lane i, 0.1 μg of poly(dI-dC) added; lane j, 0.5 μg of poly(dI-dC); lane k, 2 μg of poly(dI-dC); lane m, 5 μg of poly(dI-dC) added.