Abstract
1. The whole-cell patch clamp technique was used to investigate the swelling-activated currents in bovine non-pigmented ciliary epithelial (NPCE) cells. 2. Exposure to hypotonic solution activated a current that was blocked by 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)benzoic acid (NPPB). The I-V relationship was shifted in the direction expected for a Cl- current when the external Cl- was replaced by gluconate (permeability ratio P(gluconate)/PCl = 0.17). The inhibition of the current evoked by voltage clamp steps of +80 mV yielded an IC50 for NPPB of 13.4 microM. 3. The current was found to be dependent on ATP. With ATP in the patch pipette the current could be repeatedly activated by exposure to hypotonic solution but when ATP was omitted the current ran down with time. 4. The development of this current was associated with visible cell swelling and inhibitors of regulatory volume decrease in these cells, e.g. tamoxifen, 4-acetamido-4'-isothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid (SITS) and 4,4'-diisothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid (DIDS), also inhibited this current. 5. The volume-activated current was additionally blocked by NPPB, verapamil, quinidine and dideoxyforskolin. 6. The current was independent of external calcium and exhibited slight outward rectification and time-dependent inactivation at strong depolarizing potentials. 7. Disrupting the cytoskeleton and microtubules with cytochalasin B and colchicine had no effect on the activation of the Cl- current. 8. An antibody (C219) to the MDR1 gene product, P-glycoprotein, caused a functional block of the swelling-activated Cl- current when added to the patch pipette. 9. Immunofluorescence studies using the monoclonal antibodies C219 and JSB-1 demonstrated the presence of P-glycoprotein in the ciliary epithelial cells. The immunofluorescence was stronger on the non-pigmented than on the pigmented cells. 10. It is concluded that swelling in NPCE cells activates a Ca(2+)-independent, ATP-dependent Cl- current and that the activity of this current is associated with P-glycoprotein. 11. It is suggested that this Cl- current contributes to regulatory volume decrease and may participate in the secretory activity of these cells.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. P., Welsh M. J. Calcium and cAMP activate different chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6003–6007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baquet A., Meijer A. J., Hue L. Hepatocyte swelling increases inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, calcium and cyclic AMP concentration but antagonizes phosphorylase activation by Ca2(+)-dependent hormones. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80094-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
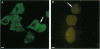
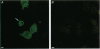
- Belles B., Malécot C. O., Hescheler J., Trautwein W. "Run-down" of the Ca current during long whole-cell recordings in guinea pig heart cells: role of phosphorylation and intracellular calcium. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):353–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00587713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxterman H. J., Pinedo H. M., Kuiper C. M., van der Hoeven J. J., de Lange P., Quak J. J., Scheper R. J., Keizer H. G., Schuurhuis G. J., Lankelma J. Immunohistochemical detection of P-glycoprotein in human tumor cells with a low degree of drug resistance. Int J Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;43(2):340–343. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Peterson-Yantorno K., Coca-Prados M., Yantorno R. E. Regulatory volume decrease by cultured non-pigmented ciliary epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 1992 Feb;54(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(05)80207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cliff W. H., Frizzell R. A. Separate Cl- conductances activated by cAMP and Ca2+ in Cl(-)-secreting epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4956–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz M., Valverde M. A., Higgins C. F., Rucăreanu C., Sepúlveda F. V. Volume-activated chloride channels in HeLa cells are blocked by verapamil and dideoxyforskolin. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jan;422(4):347–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00374290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farahbakhsh N. A., Fain G. L. Volume regulation of non-pigmented cells from ciliary epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Jun;28(6):934–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges E., Bradley G., Gariepy J., Ling V. Detection of P-glycoprotein isoforms by gene-specific monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Higgins C. F., Valverde M. A., Mintenig G. M., Sepúlveda F. V. Separation of drug transport and chloride channel functions of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90263-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooch A. J., Morgan J., Jacob T. J. Adrenergic stimulation of bovine non-pigmented ciliary epithelial cells raises cAMP but has no effect on K+ or Cl- currents. Curr Eye Res. 1992 Oct;11(10):1019–1029. doi: 10.3109/02713689209033500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. A., Plant S., Argent B. E. cAMP-regulated whole cell chloride currents in pancreatic duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C591–C602. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gründer S., Thiemann A., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. Regions involved in the opening of CIC-2 chloride channel by voltage and cell volume. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):759–762. doi: 10.1038/360759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazama A., Okada Y. Biphasic rises in cytosolic free Ca2+ in association with activation of K+ and Cl- conductance during the regulatory volume decrease in cultured human epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Aug;416(6):710–714. doi: 10.1007/BF00370619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. J., Fu W. O., Chung Y. W., Zhou T. S., Wong P. Y. Properties of cAMP-dependent and Ca(2+)-dependent whole cell Cl- conductances in rat epididymal cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):C794–C802. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.4.C794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo M., Okada Y. Volume-regulatory Cl- channel currents in cultured human epithelial cells. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:351–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckie D. B., Krouse M. E., Harper K. L., Law T. C., Wine J. J. Selection for MDR1/P-glycoprotein enhances swelling-activated K+ and Cl- currents in NIH/3T3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 1):C650–C658. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.2.C650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintenig G. M., Valverde M. A., Sepulveda F. V., Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Kirk J., Higgins C. F. Specific inhibitors distinguish the chloride channel and drug transporter functions associated with the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(4):305–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mito T., Delamere N. A., Coca-Prados M. Calcium-dependent regulation of cation transport in cultured human nonpigmented ciliary epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 1):C519–C526. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.3.C519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein A., Mack E. Volume-activated K+ and Cl- pathways of dissociated epithelial cells (MDCK): role of Ca2+. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C827–C834. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J. J., Schinkel A. H., Oude Elferink R. P., Groen A. K., Wagenaar E., van Deemter L., Mol C. A., Ottenhoff R., van der Lugt N. M., van Roon M. A. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelling J. W., Jacob T. J. Membrane potential oscillation from a novel combination of ion channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):C720–C727. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaut F., Tsuruo T., Hamada H., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Immunohistochemical localization in normal tissues of different epitopes in the multidrug transport protein P170: evidence for localization in brain capillaries and crossreactivity of one antibody with a muscle protein. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Feb;37(2):159–164. doi: 10.1177/37.2.2463300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilmann M., Kunzelmann K., Fröbe U., Cabantchik I., Lang H. J., Englert H. C., Greger R. Different types of blockers of the intermediate-conductance outwardly rectifying chloride channel in epithelia. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Jul;418(6):556–563. doi: 10.1007/BF00370571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde M. A., Díaz M., Sepúlveda F. V., Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Higgins C. F. Volume-regulated chloride channels associated with the human multidrug-resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):830–833. doi: 10.1038/355830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde M. A., Mintenig G. M., Sepúlveda F. V. Differential effects of tamoxifen and I- on three distinguishable chloride currents activated in T84 intestinal cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Dec;425(5-6):552–554. doi: 10.1007/BF00374885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P. A. Direct stimulation of adenylate cyclase by mechanical forces in S49 mouse lymphoma cells during hyposmotic swelling. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6569–6575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yantorno R. E., Carré D. A., Coca-Prados M., Krupin T., Civan M. M. Whole cell patch clamping of ciliary epithelial cells during anisosmotic swelling. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 1):C501–C509. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.2.C501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. J., Jacob T. J. ATP-activated chloride channel inhibited by an antibody to P glycoprotein. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):C1095–C1102. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.4.C1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]