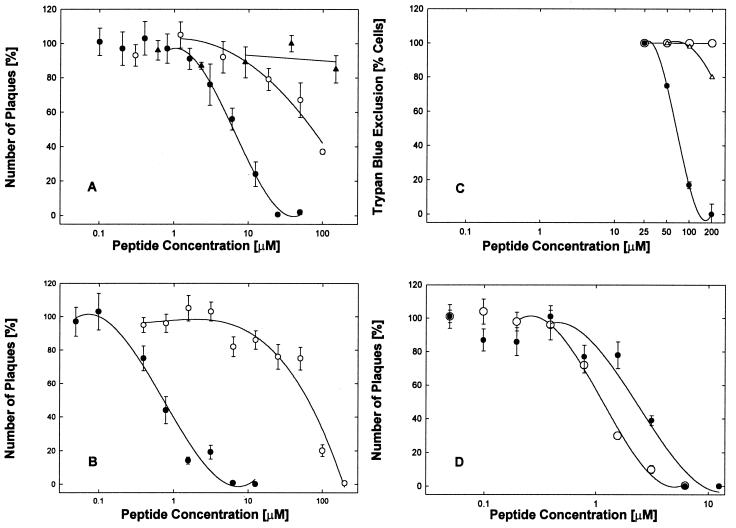
FIG. 1.
Specific antiviral and cytotoxic effects of EB and related peptides. (A and B) Antiviral activities of EB (●), EBX (○), and RRKK (▴) were compared in serum-supplemented (A) or serum-free (B) DMEM using cell cultures (2 × 105 cells/well) infected with 4000 PFU of HSV-1 KOS per well and scored for plaque formation 2 days later (control scores; 25 ± 2.5 plaques/well; n ≥ 3). Note that the effectiveness of the EB peptide (●) strongly depended on the presence of serum (IC50 = 6.4 μM [A] versus IC50 = 0.7 μM [B]) whereas that of the EBX peptide (○) did not (IC50 = 77 [A] versus IC50 = 64 [B]). (C) Cytotoxic effects were measured in uninfected cells. In serum-free medium, EB inhibited trypan blue exclusion in 50% of the cells at 68 μM (●) whereas EBX had no effect (○). In serum-supplemented medium, nearly all the cytotoxic effects of EB were alleviated (Δ). (D) Antiviral activities of EB (IC50 = 2.1 μM [●]) and EBPP (IC50 = 1.1 μM [○]) were compared in serum-free DMEM in cultures (2 × 105 cells/well) infected with 5,000 PFU of HSV-1 KOS per well. Control scores were 35 ± 3.6 plaques/well (n = 4). All points are means of three to six determinations with standard errors of the means.