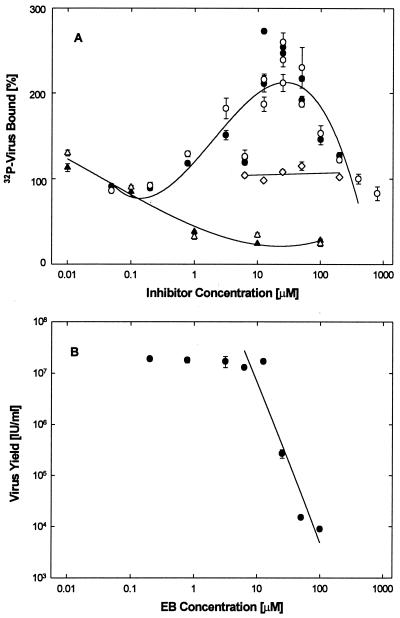
FIG. 4.
Effect of EB on virus adsorption. (A) Live (solid symbols) and formaldehyde-fixed (open symbols) cells (2 × 105 cells/well) were exposed to 32P-labeled HSV-1 KOS (2 × 104 cpm/well; 0.01 cpm/PFU) in the presence of EB (● and ○), EBX (◊), or heparin (▴ and Δ), and the bound labeled was extracted and counted (100% corresponds to ∼1.8 × 103 cpm/well). (B) Under identical conditions, cells were also infected with unlabeled HSV-1 KOS (2 × 106 PFU/well) and then returned to regular medium for 3 days before the effect of EB on virus yields was measured. Inhibition of virus production (IC50 ≈ 10 μM) coincides with maximal EB-induced virus binding (10 to 50 μM). All data points in are means of triplicate measurements with standard errors of the means (error bars are mostly smaller than the symbols).