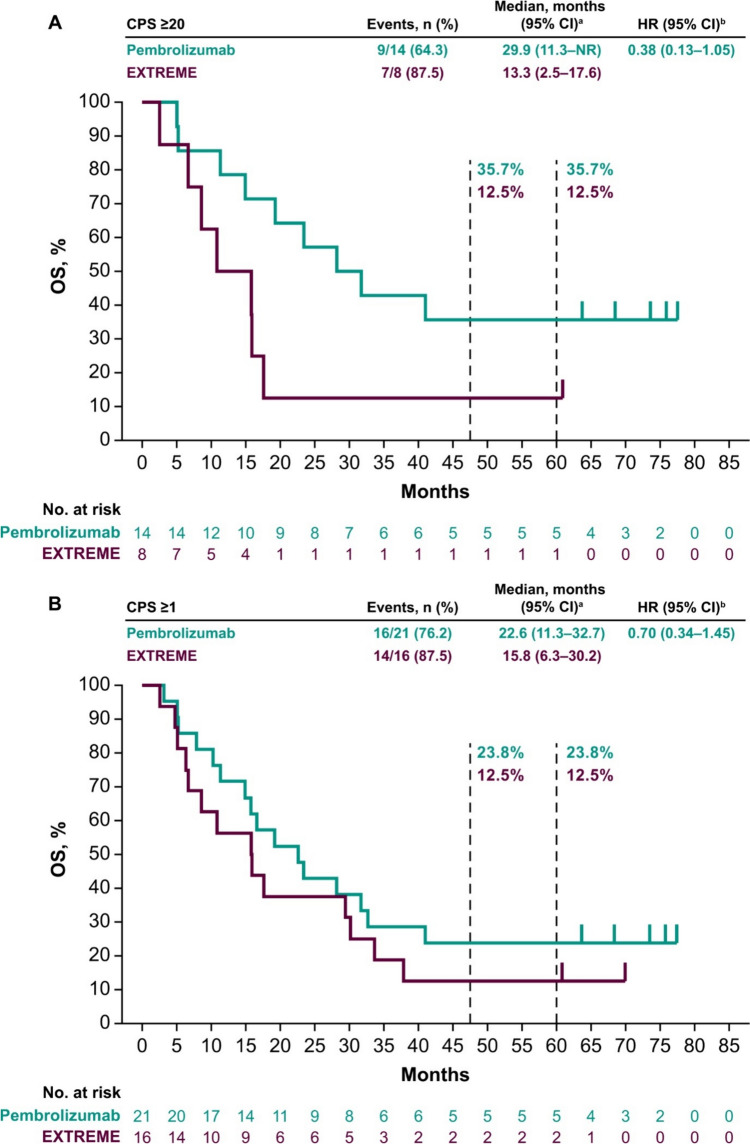
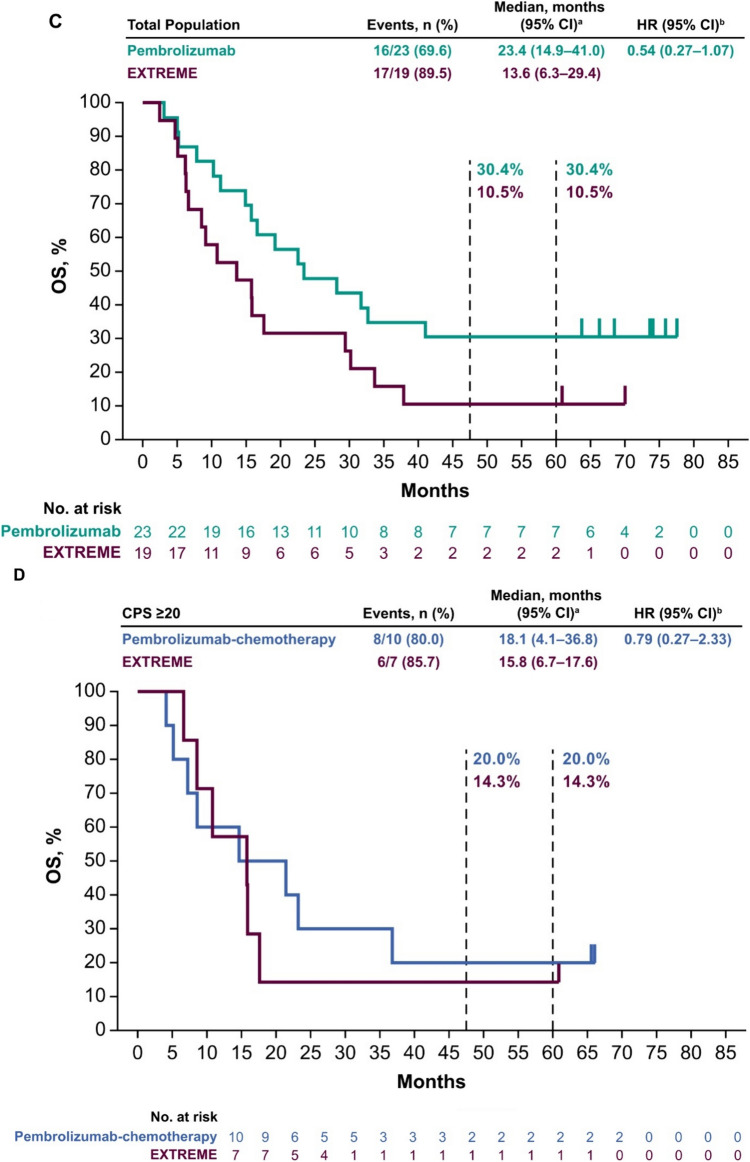
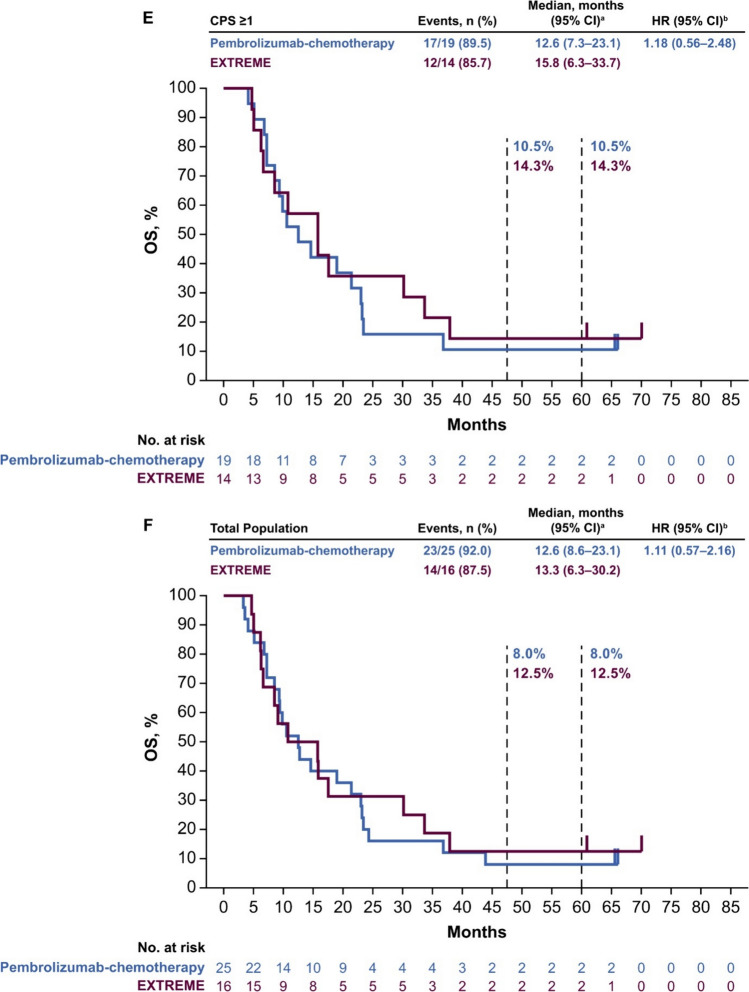
Fig. 1.
Pembrolizumab versus EXTREME in the A PD-L1 CPS ≥ 20, B PD-L1 CPS ≥ 1, and C total Japanese populations at long-term follow-up and pembrolizumab-chemotherapy versus EXTREME in the D PD-L1 CPS ≥ 20, E PD-L1 CPS ≥ 1, and F total Japanese populations. aFrom the product-limit (Kaplan–Meier) method for censored data. bOn the basis of a Cox proportional hazards regression model with the Efron method of tie handling with treatment as a covariate. CI confidence interval, CPS combined positive score, HR hazard ratio, OS overall survival, PD-L1 programmed cell death ligand 1