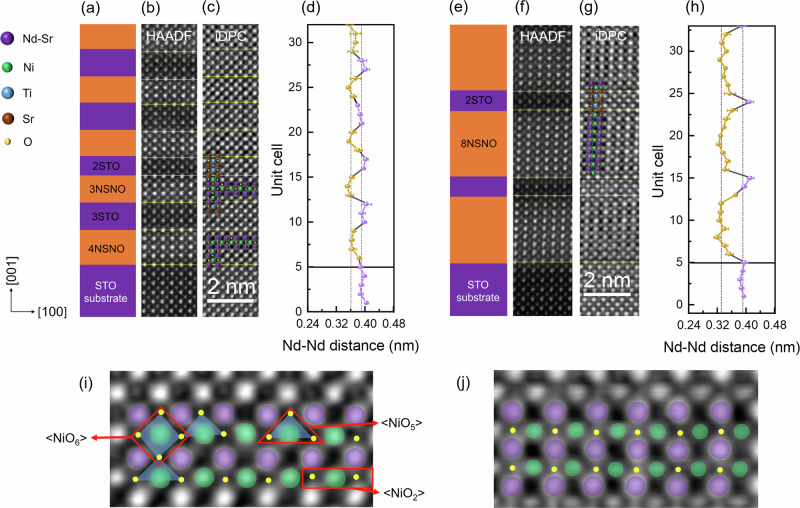
Fig. 2. High-resolution STEM images of reduced superlattices (R-Nm/S2).
a Schematic structure of the R-N3/S2 superlattice, the nickelate (NSNO) and strontium titanate (STO) layers in the superlattice are distinguished by orange and purple colors, respectively. b Atomically resolved HAADF-STEM image of R-N3/S2. c iDPC-STEM image of R-N3/S2. Different colored balls represent different atoms: Nd-Sr (purple), Ni (green), Ti (blue), Sr (brown), O (yellow). d Variation of the A-A out-of-plane distance with the number of unit cells counted from HAADF image, the colors corresponding to a are used to display the out of plane distance of various layers. e Schematic structure of the R-N8/S2 superlattice. f Atomically resolved HAADF-STEM image of R-N8/S2. g iDPC-STEM image of R-N3/S2. h Variation of the Nd-Nd out-of-plane distance with the number of unit cells counted from HAADF image. i Zoom-in iDPC-STEM image of nickelate layers in R-N3/S2. Nickelate units with different levels of reduction are indicated by shadows defined by red boxes, from left to right, rhombus (<NiO6> octahedron), triangles (<NiO5> pentahedron) and rectangles (<NiO2> infinite-layer). j Zoom-in iDPC-STEM image of nickelate layers in R-N8/S2. The error bars in d and h are calculated by averaging seven unit cells on each row.