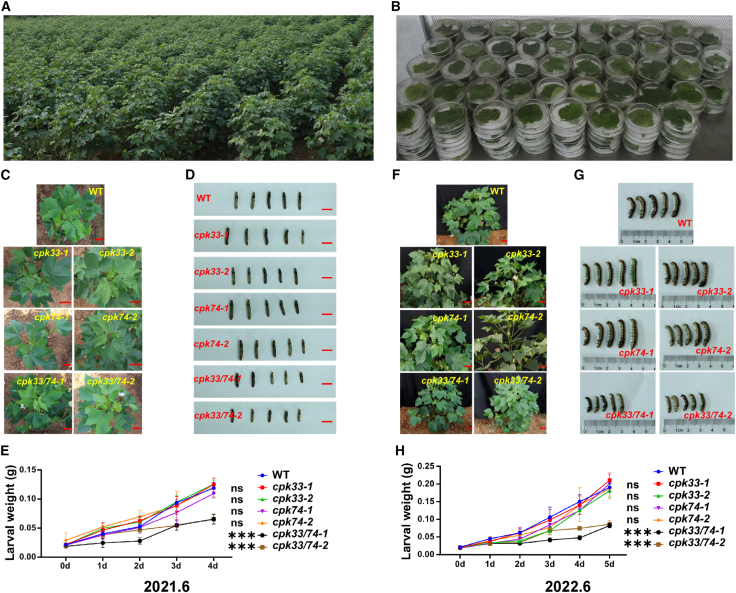
Figure 4.
Screening for materials that are resistant or sensitive to chewing pests in the GhCPK mutant library.
(A) Field phenotyping for insect resistance in materials from the GhCPK mutant library.
(B) Non-selective feeding experiment with S. litura larvae on leaves of materials from the GhCPK mutant library.
(C) Field phenotyping for insect resistance of T1-generation cpk33, cpk74, and cpk33/74 plants. The red line represents 5 cm.
(D) Comparison of body sizes of S. litura larvae after 4 days of continuous non-selective feeding on leaves of T1-generation cpk33, cpk74, and cpk33/74 plants. The red line represents 1 cm.
(E) Average weight changes in S. litura larvae after 4 days of continuous feeding on leaves of T1-generation cpk33, cpk74, and cpk33/74 plants.
(F) Field phenotyping for insect resistance of T2-generation cpk33, cpk74, and cpk33/74 plants. The red line represents 5 cm.
(G) Comparison of the body sizes of S. litura larvae after 5 days of continuous non-selective feeding on leaves of T2-generation cpk33, cpk74, and cpk33/74 plants.
(H) Average weight changes in S. litura larvae after 5 days of continuous feeding on leaves of T2-generation cpk33, cpk74, and cpk33/74 plants. Means ± SE (n = 12). Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-test. ∗∗∗p < 0.001.