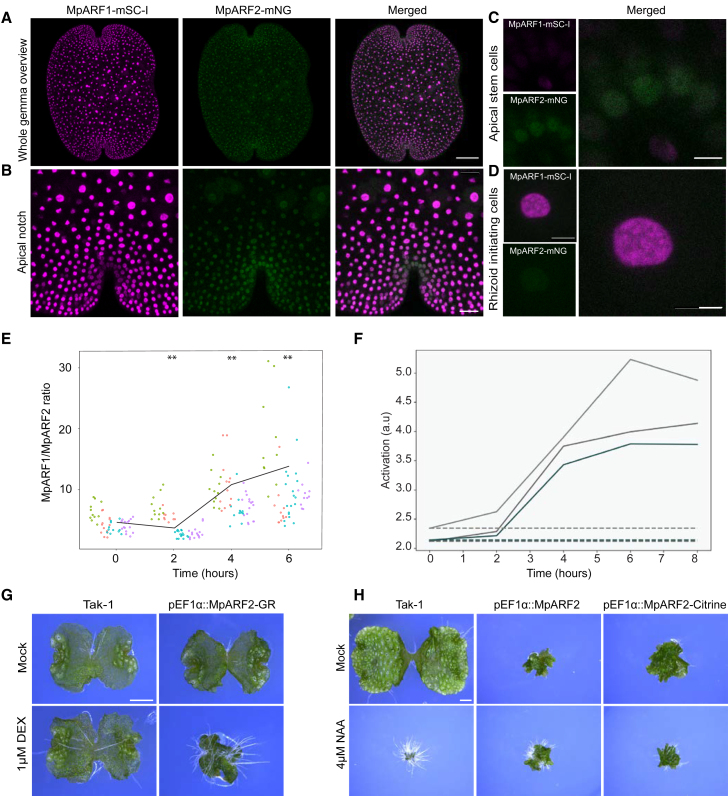
Figure 5.
Control of gemma growth by regulation of MpARF1/MpARF2 stoichiometry.
(A) Overview of MpARF1-mSC-I and MpARF2-mNG accumulation patterns in dormant gemmae of double knockin lines (scale bar, 100 μm).(B–D) Detail of MpARF1-mSC-I and MpARF2-mNG accumulation patterns in the apical notch region (B; scale bar, 25 μm), outermost apical notch cells (C; scale bar, 5 μm), and rhizoid initial cells (D; scale bar, 5 μm).(E) Quantification of ARF1:ARF2 stoichiometry in individual nuclei of a double knockin line (MpARF1-mScI MpARF2-mNG) during gemma germination. Colors mark nuclei from different gemmae. ∗∗p < 0.05, paired Student’s t test between t = 0 and other time points.(F) Predicted transcription pattern of an auxin-inducible gene (a.u.) during gemma germination. Solid lines indicate transcription rate under normal conditions in which MpARFs degrade during gemma germination, whereas dashed lines indicate transcription rate in the absence of MpARF2 proteasomal degradation. Lines correspond to predictions modeled in 3 replicate measurements of ARF levels.(G) Phenotypes of wild-type and pEF1ARF2-GR lines treated for 7 days with 1 μM dexamethasone or mock control.(H) Phenotypes of 14-day-old wild type and untagged (pEF1αARF2) or citrine-tagged (pEF1αARF2-citrine) constitutive ARF2 overexpression lines grown on mock medium or medium containing 4 μM 1-NAA. Scale bars, 1 mm.