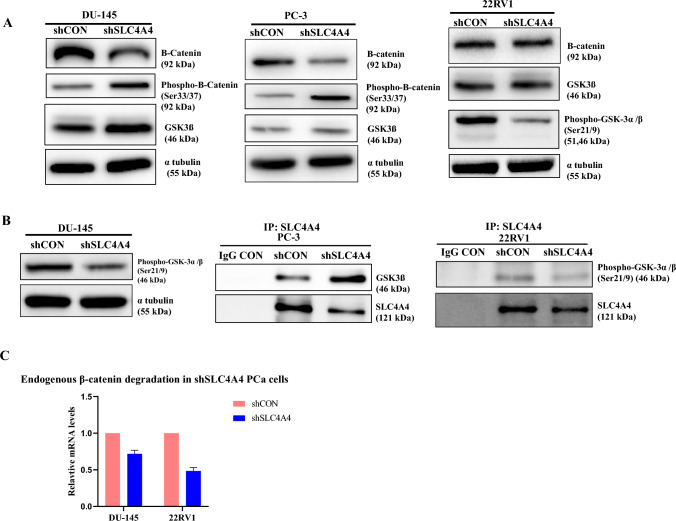
Fig. 4.
SLC4A4 knockdown restores the activity of GSK-3β and enhances phosphorylation of β-catenin in Prostate Cancer cells (A) A significant decrease in the total amount of β-catenin was found in shSLC4A4 prostate cancer cells compared to shCON. Meanwhile, the level of GSK-3β was significantly increased due to its reduced phosphorylation on residues Ser21/9 which led to increase phosphorylation (S33/37) of β-catenin (B) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) experiments showed that endogenous SLC4A4 inhibited the expression of GSK-3β. However, when prostate cancer cells were transfected with the shSLC4A4 plasmid, there was hypophosphorylation of GSK-3β at Ser21/9, which activated the total GSK-3β to degrade endogenous β-catenin (C) qPCR data confirmed the degradation of endogenous β-catenin in shSLC4A4 prostate cancer cells.