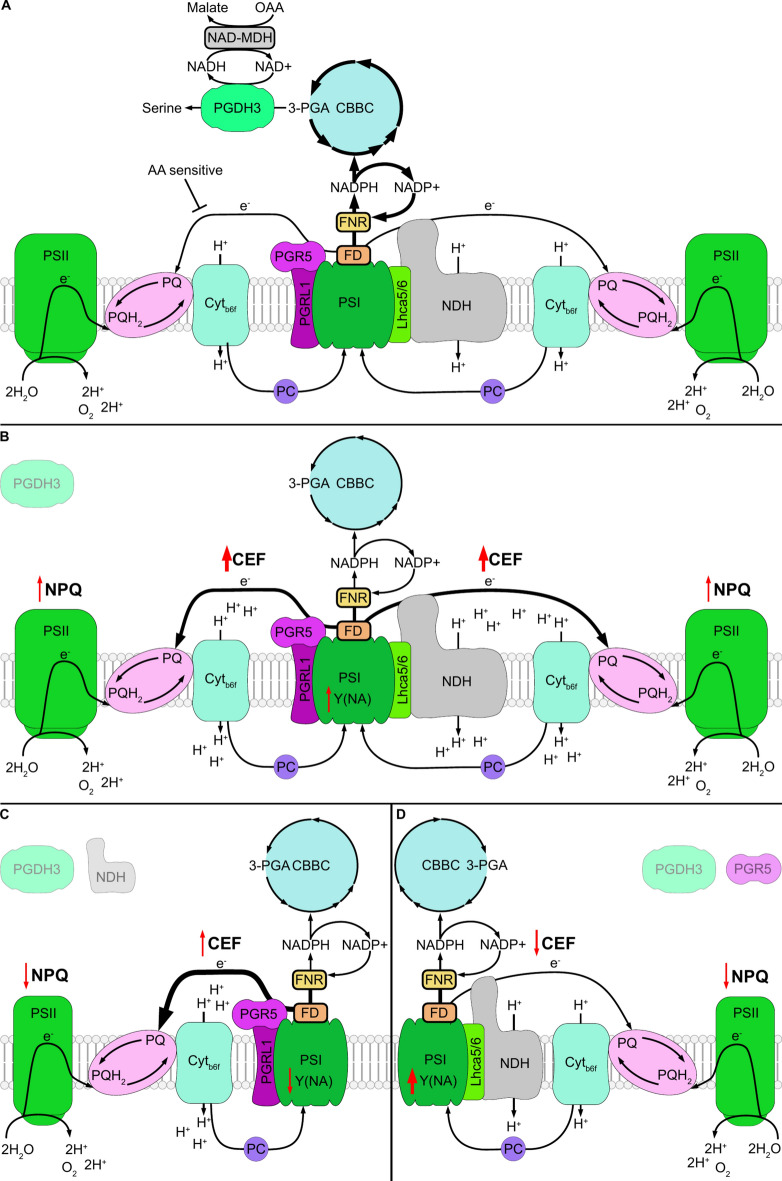
Fig. 6.
Mutant models showing the functional link between the PGDH3-permitted electron sink and CEF. By linear electron flow (LEF) electrons (e-) are directed from photosystem II (PSII) by the reduction of plastoquinone (PQ) to plastoquinol (PQH2) over the cytochrome b6f complex (Cytb6f) and subsequent reduction of plastocyanin (PC) to photosystem I (PSI). Cytb6f transfers the two H+ from PQH2 to the thylakoid lumen generating a proton motive force and a ΔpH. Following LEF the electrons can be transferred from PSI to ferredoxin (FD) and be released to the stroma via ferredoxin NADP reductase (FNR) generating NADPH from NADP+ and thereby fueling amongst other processes the Calvin Benson Bassham cycle (CBBC). 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) synthesized in the CBBC can be used by PHOSPHOGLYCERATE DEHYDROGENASE3 (PGDH3) as substrate in the first enzymatic step towards serine biosynthesis. PGDH3 generates in this step NADH from NAD+ which can then energize the NAD-Malate-Dehydrogenase (NAD-MDH) to convert oxaloacetic acid (OAA) into Malate. As an alternative to LEF, electrons can be cycled back to the PQ-Pool via two CEF routes. In the AA-sensitive route electrons are transferred from FD by the proton gradient regulation 5 (PGR5) PGR5-like photosynthetic phenotype 1 (PGRL1) complex to PQ. The second route is dependent on the NADH dehydrogenase-like (NDH) complex bound via light-harvesting complex I subunits 5 and 6 Lhca5/6 to PSI forming the PSI-NDH supercomplex. This supercomplex cycles back electrons from FD to the PQ-Pool while transporting H+ from the stroma to the lumen. The thickness of the black arrows indicates the electron flux from PSI to CBBC, PGR5, and the NDH complex. Red arrows indicate changes to different photosynthetic parameters. Models of LEF and CEF in the WT (A) and the impact on both caused by loss of PGDH3 (B), PGDH3 in combination with the NDH complex (C), and PGDH3 and PGR5 (D) are depicted.