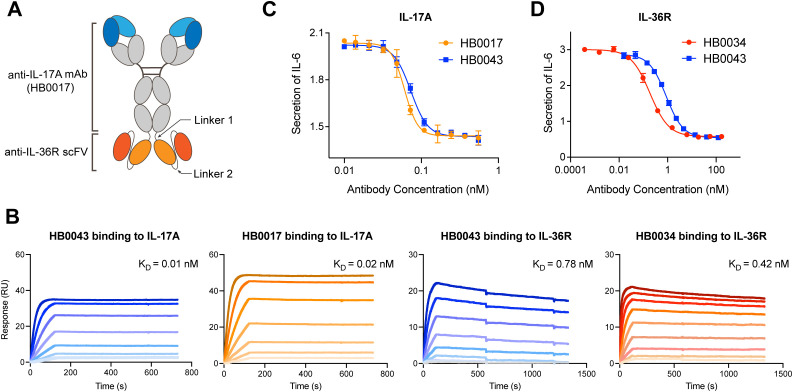
Figure 1.
HB0043 retained the affinities and blockade activity to both targets. (A) Schematics of the anti-IL-36R×IL-17A BsAb (HB0043) structure. HB0043 was constructed by linking a scFv targeting IL-36R to the C-terminal domain of the anti-IL-17A IgG backbone. (B) The kinetics profile of HB0043 and HB0017 (the parental anti-IL-17A mAb) binding to human IL-17A, and human IL-36R binding to HB0043 and HB0034 (the parental anti-IL-36R mAb) measured by SPR assay. (C) The ability of HB0043 to neutralize IL-17A signaling was measured and compared to that of HB0017, using an IL-17A blockade cell-based assay. The secretion of IL-6 was monitored, which was induced by human IL-17A (0.3 nM) and TNF-α (0.6 nM) in HT-1080 cell. (D) The inhibition of IL-6 releases from NCI/ADR-RES cells was used as an evaluation of IL-36R signaling inhibition. NCI/ADR-RES cells were stimulated with human IL36α (13.5 nM) in the presence of HB0043 (32 pM to 245 nM) and HB0034 (4 pM to 336 nM).