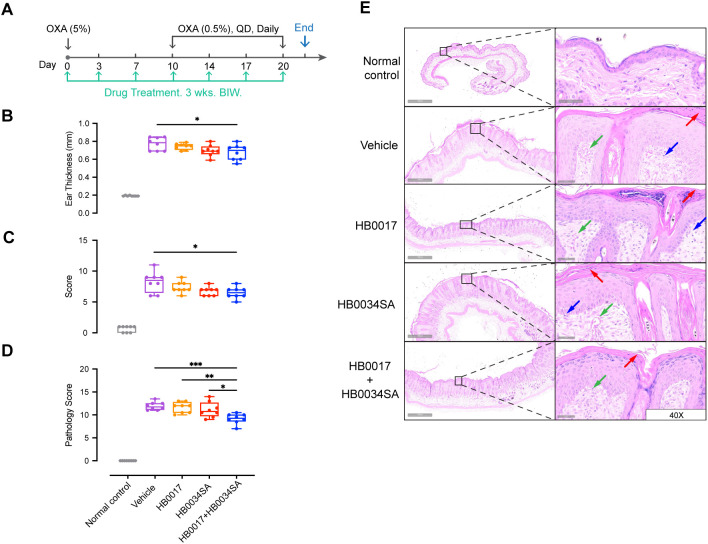
Figure 4.
The combination of mAbs targeting IL-17A and IL-36R showed stronger inhibition of inflammation relative to mAbs alone in oxazolone-induced mouse atopic dermatitis model. (A) Male C57BL/6J mice were smeared with 5.0% OXA on the shaved back skin and ear on Day0 and followed by a daily topical application of 5.0% OXA on back and 0.5% OXA on ear for thirteen consecutive days from Day7 for acute disease induction. Antibodies (HB0017, HB0034SA, HB0017+HB0034SA) were administered intraperitoneally into mice at 50 mg/kg twice a week. The control group received PBS intraperitoneal injections. (B, C) Combination of anti-IL-36R and anti-IL-17A antibodies significantly ameliorated OXA induced increase of ear thickness (B) and reduced the clinical score of back skin (C). Clinical score: the comprehensive evaluation of oedema, erythema, dryness and excoriation and each symptom was scored independently on a scale from 0 to 3: 0, none; 1, slight; 2, moderate; 3, severe. Data are expressed as min to max, n=8. *p ≤ 0.05. (D, E) Back skin samples were collected for subsequent histopathological evaluation (D) and H&E staining (E). Vehicle group: HE staining shows hyperkeratosis, significant thickening of the stratum corneum, acanthosis, and local finger-like protrusions of the epidermis into the dermis. The dermis is edematous, the capillaries are dilated and congested, and accompanied by a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration. HB0017 and HB0034SA group shows slightly improvement with mild inflammatory cell infiltration, organic lesions in corneum and dermis haven’t shown remission. HB0017+HB0034SA group: Significantly reduced hyperkeratosis and thickening of stratum corneum. Vasodilatation—green arrow; Lymphocytes—blue arrow; Hyperkeratosis/parakeratosis—red arrow. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.01.