Abstract
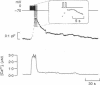
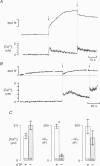
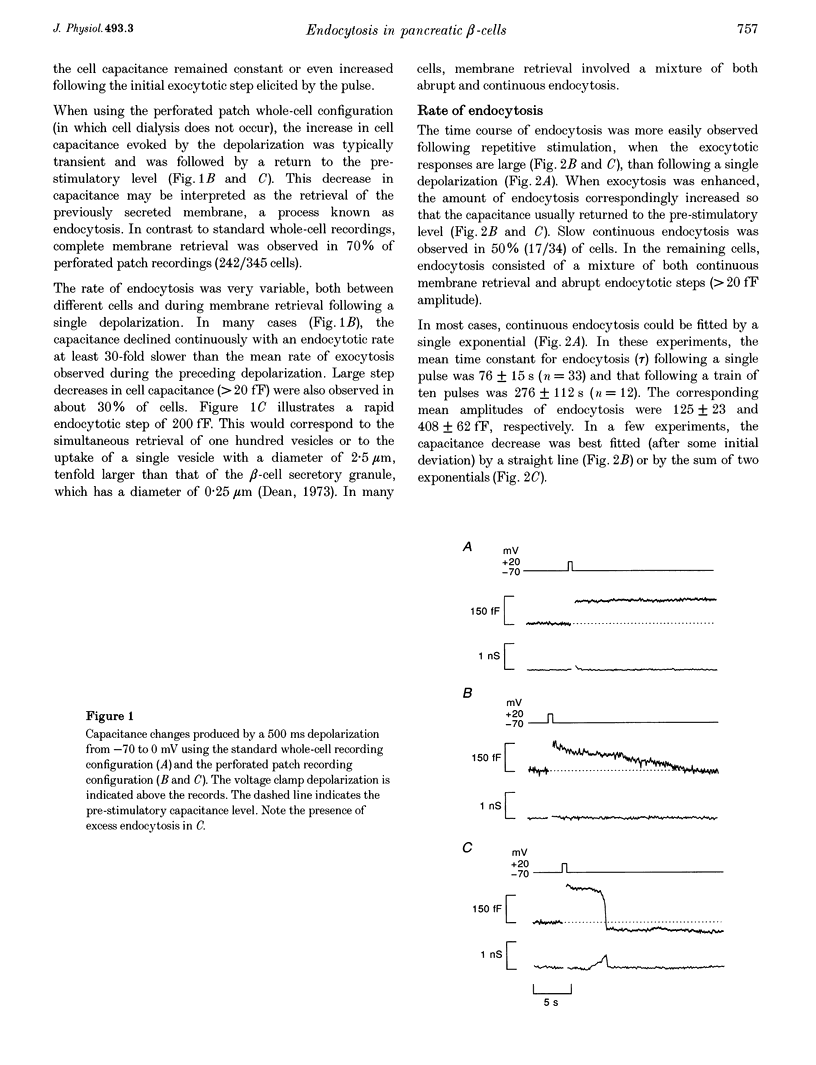
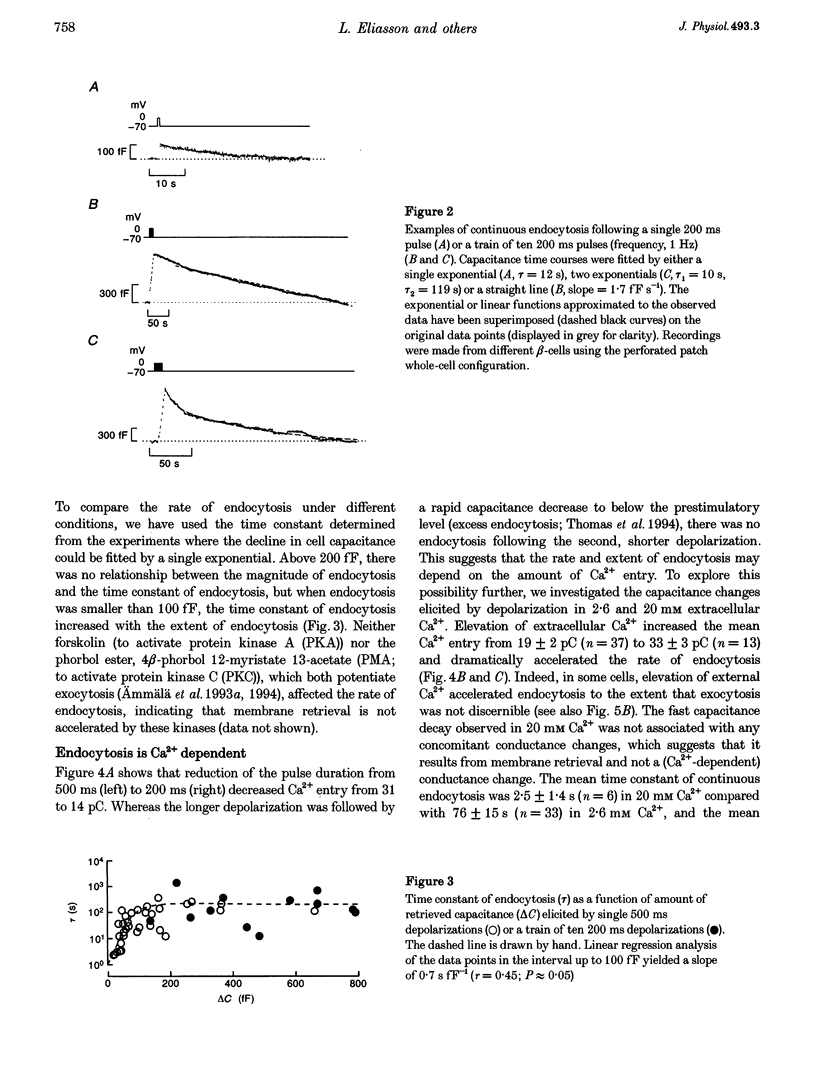
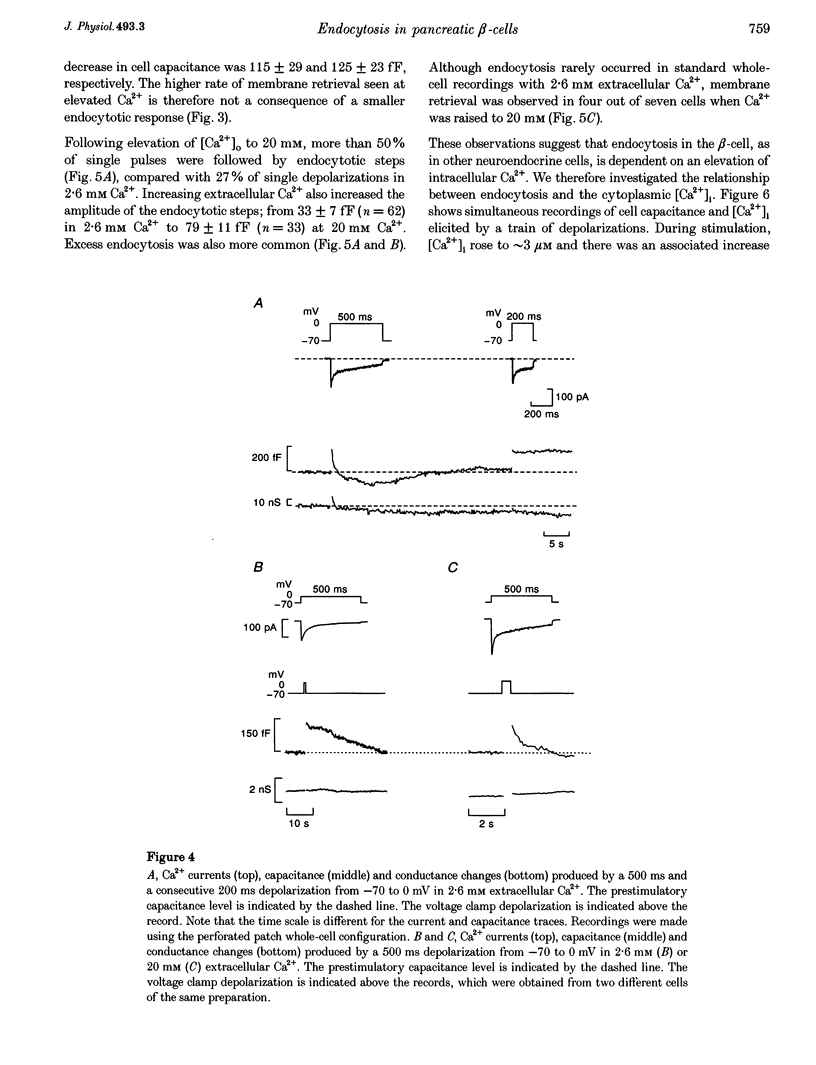
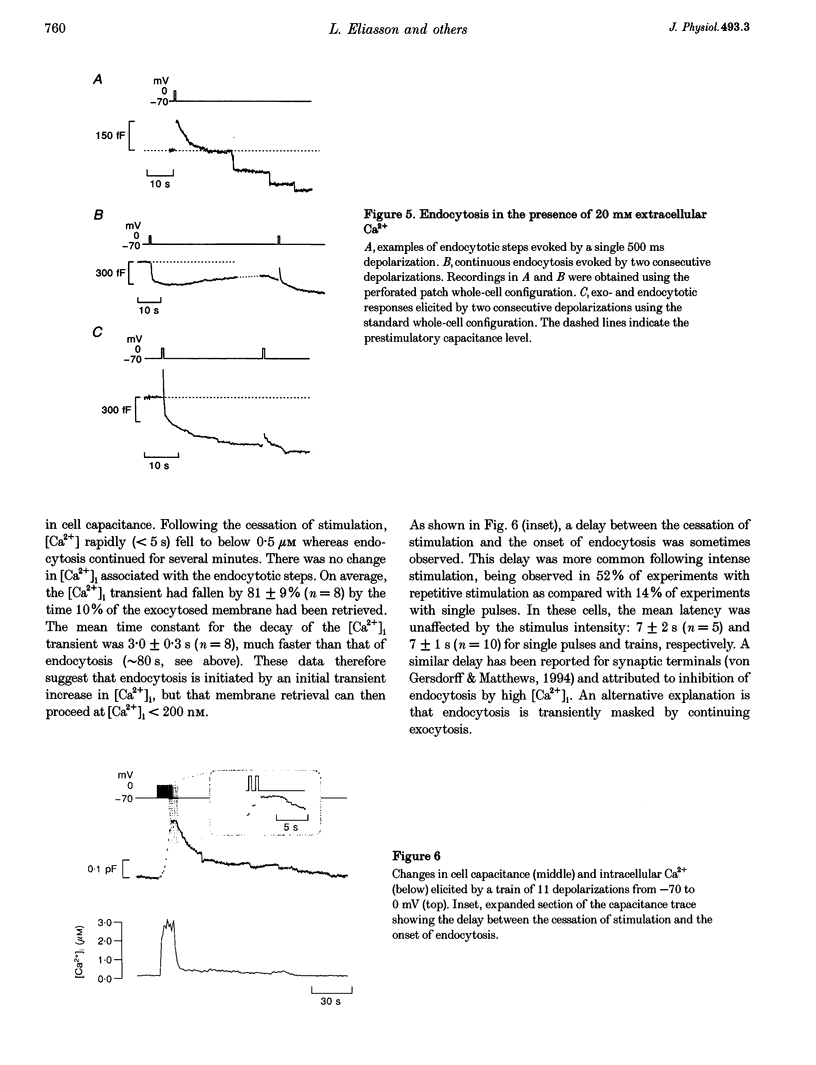
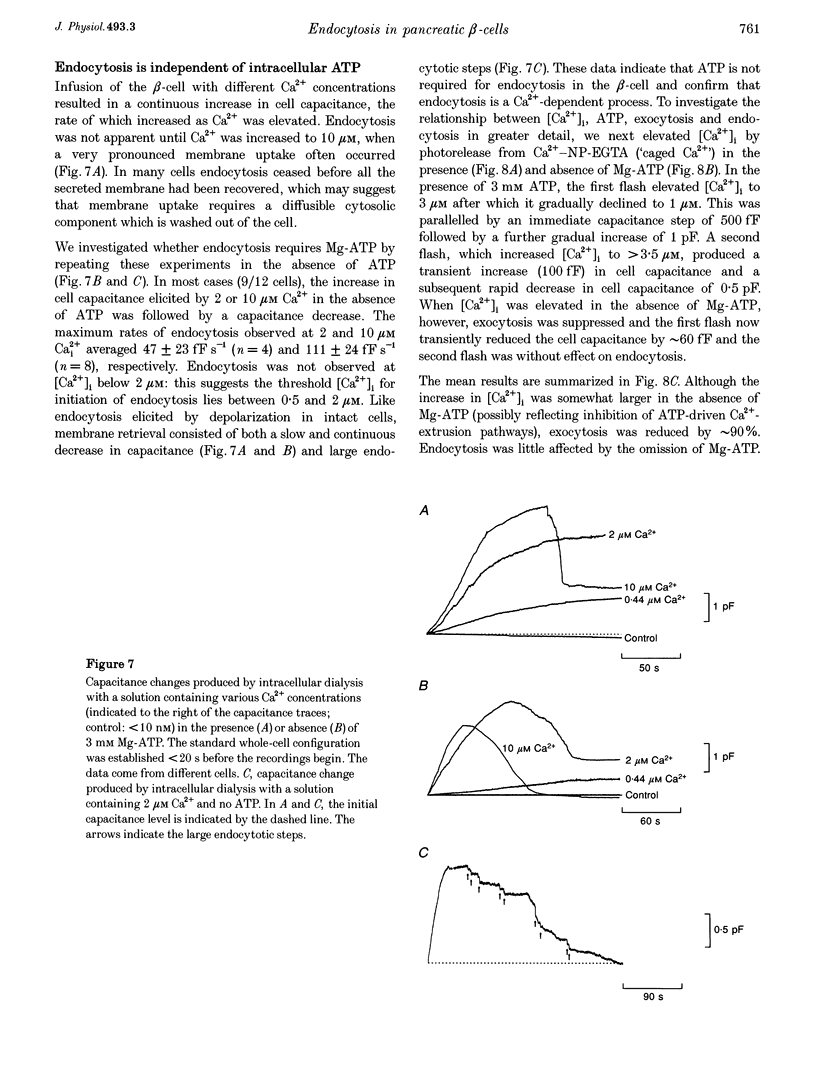
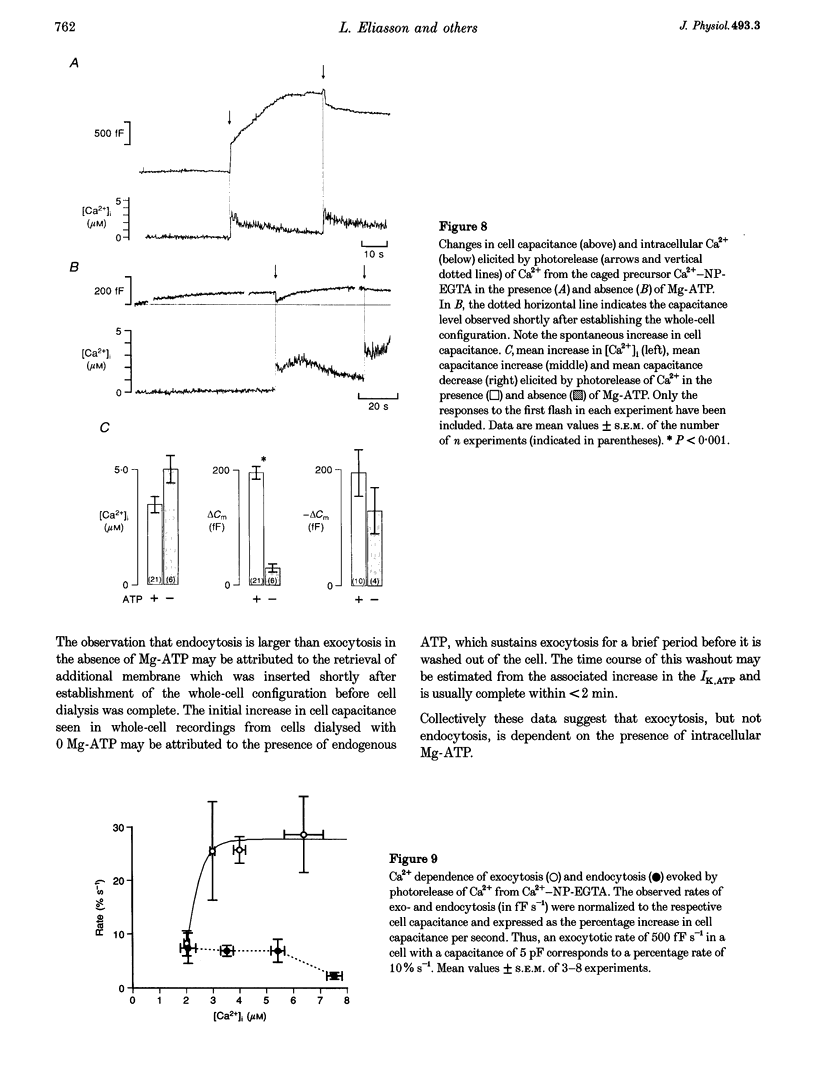
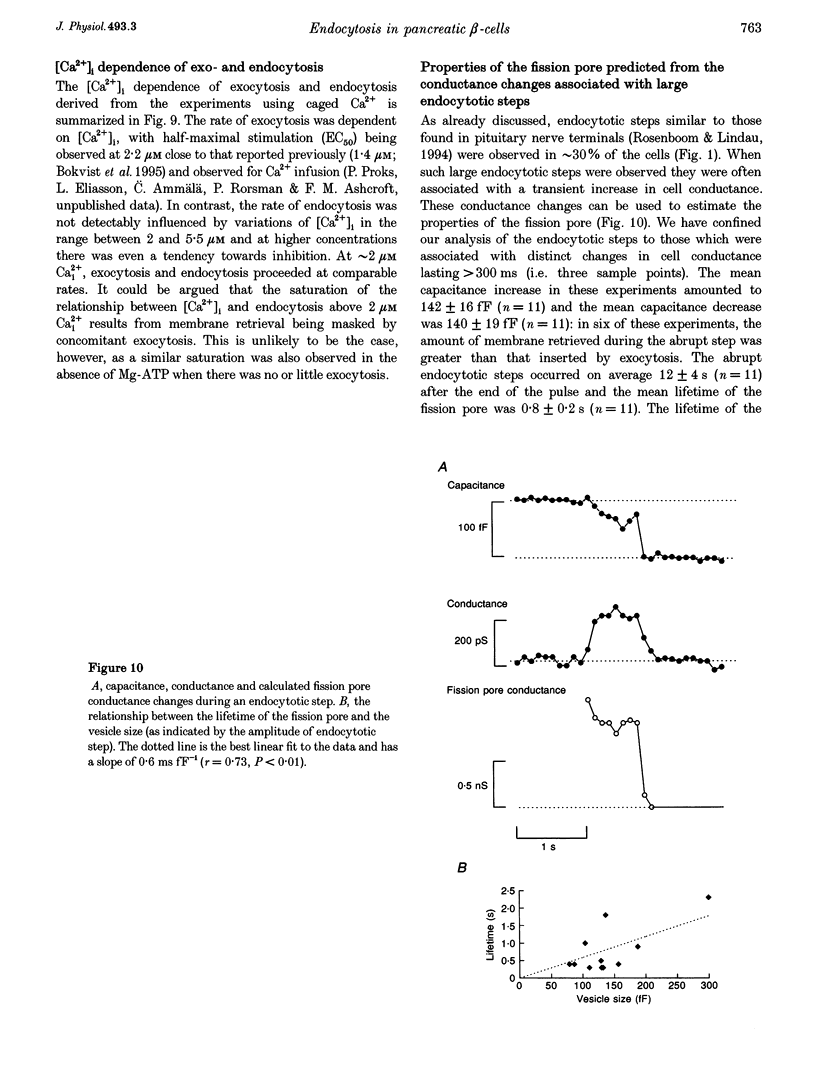
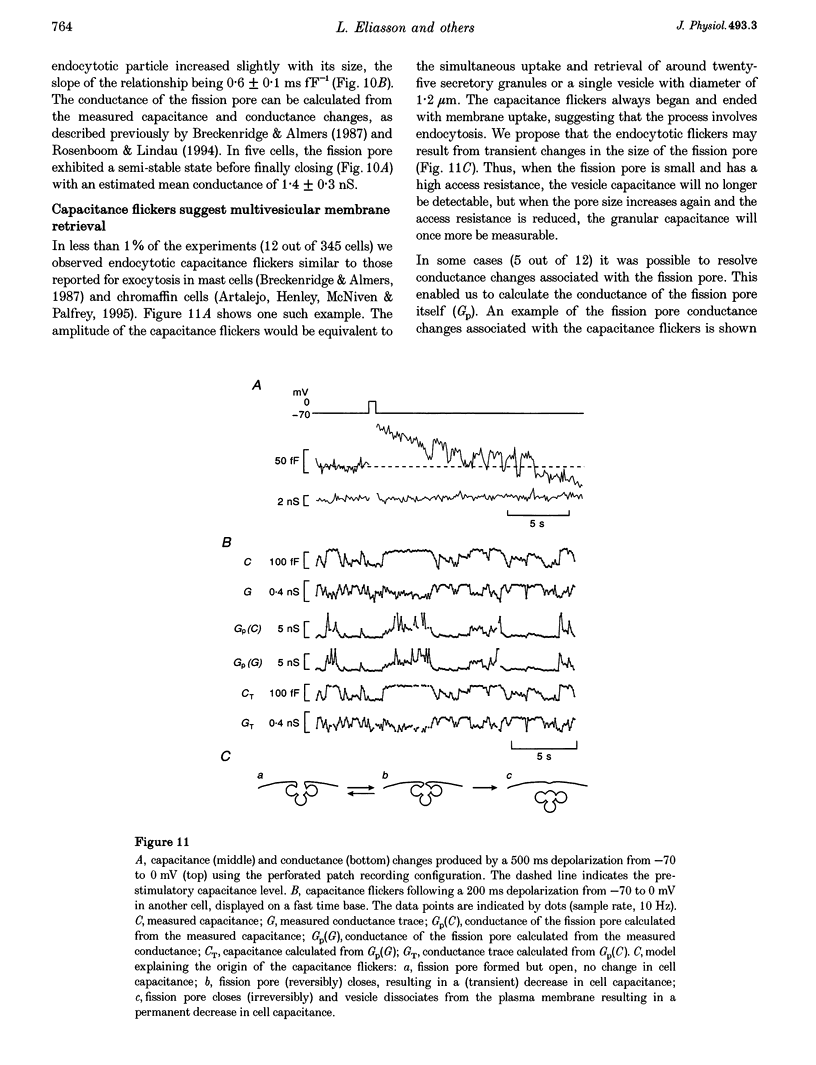
1. To investigate the mechanisms regulating the reuptake of secretory granule membranes following regulated exocytosis, we have monitored changes in cell capacitance in single pancreatic beta-cells. 2. Membrane retrieval (endocytosis) occurred both in a continuous manner and in abrupt steps, corresponding to the simultaneous retrieval of 50-100 granules. The large endocytotic steps were associated with a conductance change of about 1 nS which we attribute to the formation of a fission pore with a pore radius of approximately 1 nm. 3. In some cells, we observed large amplitude capacitance fluctuations, suggesting that aggregates of granules are connected to the plasma membrane by a single pore and are subsequently retrieved as a single unit. 4. Endocytosis was evoked by elevation of cytosolic [Ca2+]i, but once initiated, a sustained increase in [Ca2+]i was not required for endocytosis to continue. 5. The [Ca2+]i dependence of exo- and endocytosis was studied by photorelease of Ca2+ from the 'caged' precursor Ca(2+)-nitrophenyl-EGTA (Ca(2+)-NP-EGTA). Both exo- and endocytosis were initiated at between 0.5 and 2 microM Cai(2+). The rate of endocytosis saturated above 2 microM Cai(2+), whereas exocytosis continued to increase up to 4 microM Cai(2+). The maximum rate of endocytosis was < 25% of that of exocytosis. 6. Unlike exocytosis, endocytosis proceeded equally well in the presence or absence of Mg-ATP. 7. Our data indicate that in the pancreatic beta-cell, exocytosis and endocytosis are regulated by different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez de Toledo G., Fernández-Chacón R., Fernández J. M. Release of secretory products during transient vesicle fusion. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):554–558. doi: 10.1038/363554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammälä C., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Calcium-independent potentiation of insulin release by cyclic AMP in single beta-cells. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):356–358. doi: 10.1038/363356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammälä C., Eliasson L., Bokvist K., Berggren P. O., Honkanen R. E., Sjöholm A., Rorsman P. Activation of protein kinases and inhibition of protein phosphatases play a central role in the regulation of exocytosis in mouse pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4343–4347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammälä C., Eliasson L., Bokvist K., Larsson O., Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Exocytosis elicited by action potentials and voltage-clamp calcium currents in individual mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol. 1993 Dec;472:665–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Henley J. R., McNiven M. A., Palfrey H. C. Rapid endocytosis coupled to exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells involves Ca2+, GTP, and dynamin but not clathrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8328–8332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Kakei M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat pancreatic beta-cells: modulation by ATP and Mg2+ ions. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:349–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Neher E. Calcium requirements for secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:247–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Holz R. W. Kinetic analysis of secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells reveals distinct components. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16219–16225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokvist K., Eliasson L., Ammälä C., Renström E., Rorsman P. Co-localization of L-type Ca2+ channels and insulin-containing secretory granules and its significance for the initiation of exocytosis in mouse pancreatic B-cells. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):50–57. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06974.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge L. J., Almers W. Currents through the fusion pore that forms during exocytosis of a secretory vesicle. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):814–817. doi: 10.1038/328814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Fast exocytosis and endocytosis triggered by depolarisation in single adrenal chromaffin cells before rapid Ca2+ current run-down. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Jun;430(2):213–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00374652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran M. J., Cohen F. S., Chandler D. E., Munson P. J., Zimmerberg J. Exocytotic fusion pores exhibit semi-stable states. J Membr Biol. 1993 Apr;133(1):61–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00231878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis-Davies G. C., Kaplan J. H. Nitrophenyl-EGTA, a photolabile chelator that selectively binds Ca2+ with high affinity and releases it rapidly upon photolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):187–191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann C., Chow R. H., Neher E., Zucker R. S. Kinetics of the secretory response in bovine chromaffin cells following flash photolysis of caged Ca2+. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2546–2557. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80744-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Marty A. Discrete changes of cell membrane capacitance observed under conditions of enhanced secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6712–6716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Zucker R. S. Multiple calcium-dependent processes related to secretion in bovine chromaffin cells. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90238-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malaisse-Lagae F., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Renold A. E. Exocytosis-endocytosis coupling in the pancreatic beta cell. Science. 1973 Aug 10;181(4099):561–562. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4099.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Malaisse W. Hypothesis: single and chain release of insulin secretory granules is related to anionic transport at exocytotic sites. Diabetes. 1980 Nov;29(11):943–944. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.11.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons T. D., Lenzi D., Almers W., Roberts W. M. Calcium-triggered exocytosis and endocytosis in an isolated presynaptic cell: capacitance measurements in saccular hair cells. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):875–883. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proks P., Ashcroft F. M. Effects of divalent cations on exocytosis and endocytosis from single mouse pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol. 1995 Sep 1;487(Pt 2):465–477. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae J., Cooper K., Gates P., Watsky M. Low access resistance perforated patch recordings using amphotericin B. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Mar;37(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90017-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Wollheim C. B., Lang J., Theler J. M., Rossetto O., Montecucco C., Sadoul K., Weller U., Palmer M., Thorens B. VAMP-2 and cellubrevin are expressed in pancreatic beta-cells and are essential for Ca(2+)-but not for GTP gamma S-induced insulin secretion. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2723–2730. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Bokvist K., Ammälä C., Eliasson L., Renström E., Gäbel J. Ion channels, electrical activity and insulin secretion. Diabete Metab. 1994 Mar-Apr;20(2):138–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenboom H., Lindau M. Exo-endocytosis and closing of the fission pore during endocytosis in single pituitary nerve terminals internally perfused with high calcium concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5267–5271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. Photorelease techniques for raising or lowering intracellular Ca2+. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;40:31–63. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]