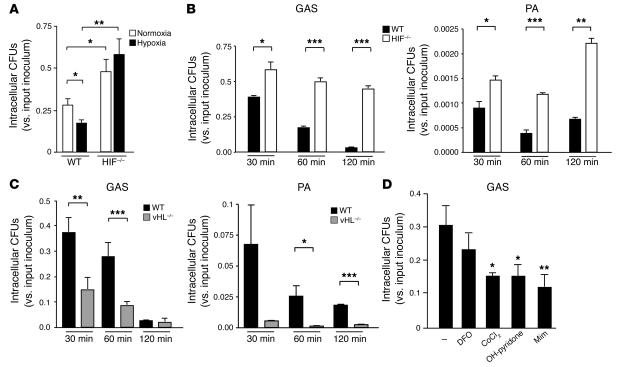
Figure 2.
HIF-1α regulates bactericidal activity of myeloid cells. (A) Intracellular killing of GAS by WT, HIF-1α–null, or vHL-null macrophages. BM-derived macrophages were inoculated with GAS at an MOI equal to 2.5 and cultured under normoxic (white bars) or hypoxic (0.1%; black bars) conditions for 1 hour after antibiotic treatment. Statistical analyses were performed using unpaired Student’s t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (B) Loss of HIF-1α in macrophages decreases intracellular killing of GAS and of P. aeruginosa. WT (black bars) or HIF-1α–null (white bars) BM-derived macrophages were incubated with bacteria for 1 hour before antibiotics were added. Intracellular killing was analyzed by determination of viable CFUs in macrophage lysates at the specified time points after bacterial uptake. Experiments were performed in triplicate. SEM is displayed. Experiment shown is representative of 3 repeated studies. (C) Loss of vHL in BM-derived macrophages increases intracellular killing of GAS and of P. aeruginosa. Experiments were performed in triplicate and are representative of 3 repeated studies. SEM is displayed. (D) Pharmacologic agonists of HIF-1α increase myeloid cell bactericidal activity. Preincubation (5 hours) with desferrioxamine mesylate (DFO), CoCl2, OH-pyridone, or Mim increased the intracellular killing capacity of WT macrophages against GAS. ***P < 0.001.