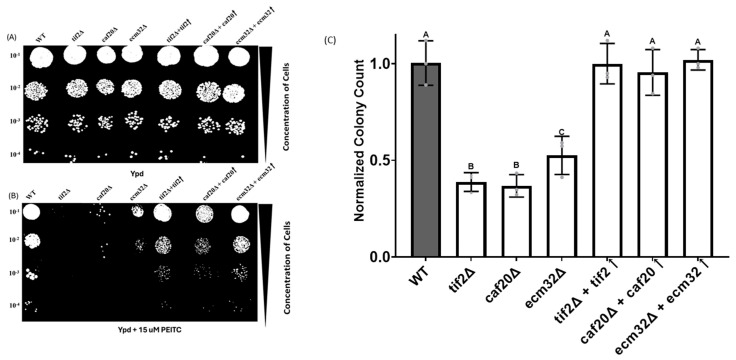
Figure 3.
The spot test and colony count analysis showed increased sensitivity to PEITC for the tif2∆, caf20∆, and ecm32∆ yeast strains compared with the wild-type. (A,B) Serially diluted yeast cells (10−1 to 10−4) and cells spotted onto YPD media and YPD media with 15 μM PEITC, respectively. The gene deletion mutants caf20∆ and ecm32∆ had reduced growth in the presence of PEITC, in (B) when compared with PEITC-free conditions. tif2∆ was used as a positive control. Partial phenotypic rescue was observed in the mutant strains when the respective target gene was restored by using a plasmid. (C) Colony count analysis in PEITC growth medium. Mutant deletion strains had a significantly reduced number of colonies in the presence of PEITC compared with the wild-type. Mutant strains with reintroduced genes had colony counts similar to the wild-type. p-Values of tif2∆ = 1.86 × 10−7, caf20∆ = 6.41 × 10−6, and ecm32∆ = 9.74 × 10−6 were obtained, with all other results being insignificant. Letters above the bars indicate statistical significance. Bars that share the same letter do not have a significant difference between them, while bars with different letters have a significant difference between them. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the data are presented as the mean values, with bars representing the standard deviations (SDs). Statistical analysis was performed by using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), with multiple comparisons followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. A p-value < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.