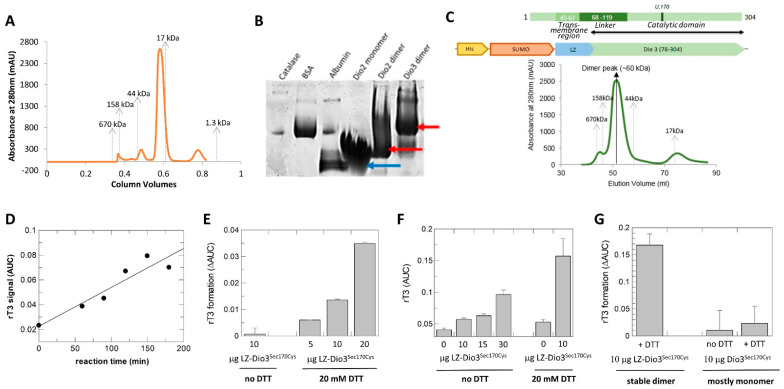
Figure 4.
Dio dimerization and activity. (A) SEC profile of mDio2-71-262. Elution positions of molecular weight standards are indicated. (B) Blue native PAGE of Dio2 samples eluted from SEC at the size corresponding to monomer or dimer, respectively. For comparison, catalase (240 kD), bovine serum albumin (67 kD), and chicken egg albumin (45 kD) are shown. The Dio3 dimer represents LZ-mDio3 (see panel C). Arrows indicate main positions of the Dio bands. (C) Engineering of a stable mDio3-cat dimer. Schemes of the mDio3 domains (black double-arrow: length of mDio2cat construct) and the fusion construct with a dimerizing Leu zipper (LZ). Below the schemes, a SEC profile of the purified LZ-mDio3-cat construct is shown. Elution positions of molecular weight standards are indicated. (D) Time-dependent increase in rT3 formed from T4 by LZ-mDio3-cat in presence of DTT. (E) Increase in rT3 formation in presence of increasing enzyme amounts in presence of DTT. (F) Enzyme-dependent increase in product rT3 in absence of DTT (left), and substantial increase in product formation in presence of the redox cofactor (right). (G) Comparison of rT3 formation by the stable LZ-mDio-cat dimer (left) and the mostly monomeric mDio3-cat (right).