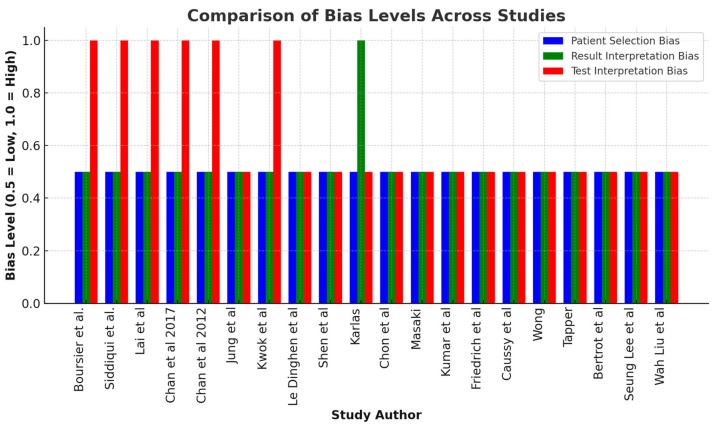
Figure 1.
The bar chart above visualizes the comparison of bias levels across different studies. Blue bars represent the risk of bias in patient selection, which is consistently low across all studies. Green bars indicate the risk of bias in result interpretation, with only Karlas et al. [18] showing a high level of bias in this category. Red bars represent the risk of bias in test and reference test interpretation. Several studies, including Boursier et al. [9], Siddiqui et al. [10], Lai et al. [11], and both Chan et al. [12,13] studies, exhibit high bias here, while others, like Jung et al. [14] and Wong et al. [24], show low bias [15,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,25,27,28,29].