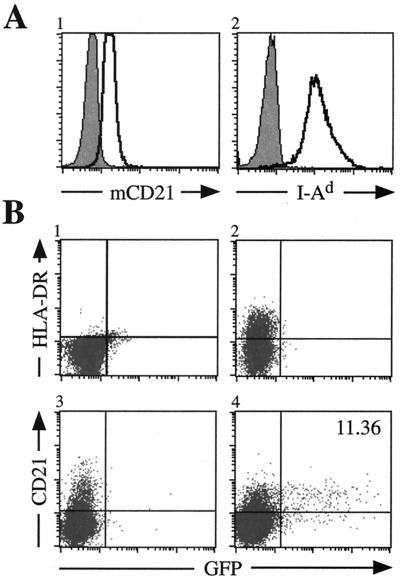
FIG. 1.
EBV infection of M12 cells is dependent upon the dual expression of hCD21 and HLA class II. (A) Surface expression of mCD21 and I-Ad (clear histograms) on M12 cells analyzed by flow cytometry. mCD21 expression was determined using an anti-mCD21 antibody directly conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate (Pharmingen). I-Ad was observed by staining cells with a biotin-conjugated anti-I-Ad antibody (Pharmingen) detected by streptavidin-conjugated allophycocyanin (APC) (Pharmingen). Shaded histograms represent cells stained with an isotype-matched control antibody. (B) Susceptibility of M12 cells to EBfaV-GFP infection. pSG5 (Stratagene)-transfected cells do not express HLA-DR (panel 1) or hCD21 (data not shown) and are resistant to EBV infection. M12 cells transiently expressing HLA-DR (panel 2) or hCD21 (panel 3) are inefficiently infected with EBV. However, M12 cells expressing both hCD21 and HLA-DR (panel 4) are efficiently infected by EBfaV-GFP. A20 and M12 cells were infected by EBfaV-GFP as previously described 24 h after transfection (12, 13). Analysis of infected cells occurred 24 h after infection. HLA-DR expression was observed using an anti-HLA-DR antibody directly conjugated to APC (Becton Dickinson); hCD21 expression was recognized by a biotin-conjugated anti-hCD21 antibody (Ancell) detected using streptavidin-conjugated APC.