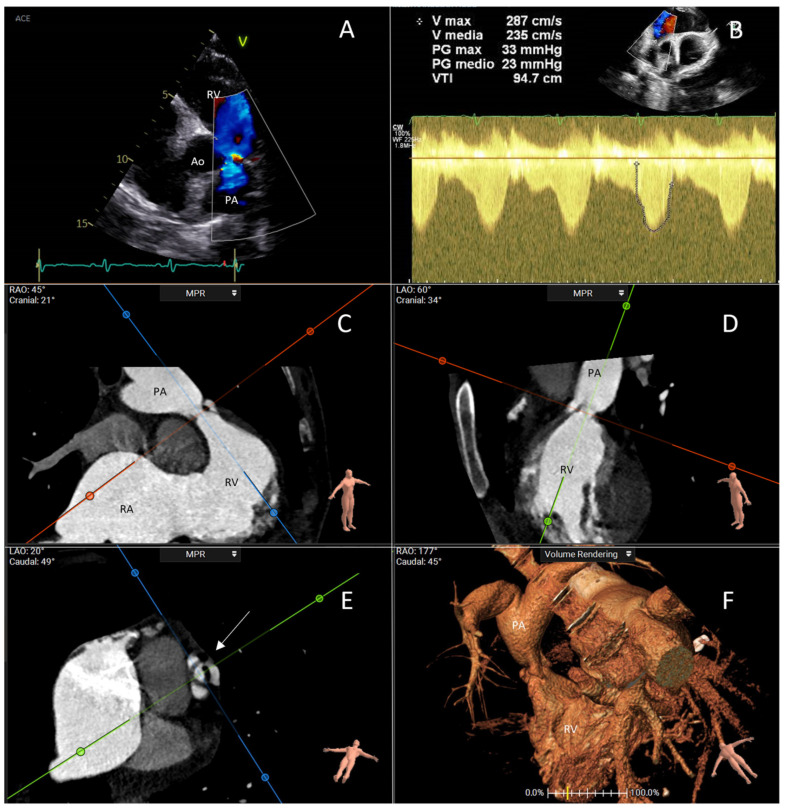
Figure 2.
This figure represents a case evaluated at Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Campus Bio-Medico, Rome. It is about a 51-year-old woman who had severe pulmonary valve stenosis and torrential tricuspid regurgitation in the setting of carcinoid heart disease. (A) The transthoracic echocardiogram with color Doppler shows turbulence in blood flow across the stenotic pulmonary valve. (B) Continuous-wave Doppler examination shows a typical curve of severe pulmonary stenosis with increased gradient across the valve; this was a case of low-flow–low-gradient pulmonary stenosis because of the coexistence of torrential tricuspid regurgitation. (C–E) CT scan examination with multiplanar reconstruction in systole reveals the morphology of the pulmonary valve (arrow), showing thickened and hypomobile cusps. (F) Three-dimensional volume rendering showing the narrowed pulmonary valve and the post-stenotic dilation of the pulmonary artery. Ao: aorta; PA: pulmonary artery; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle.