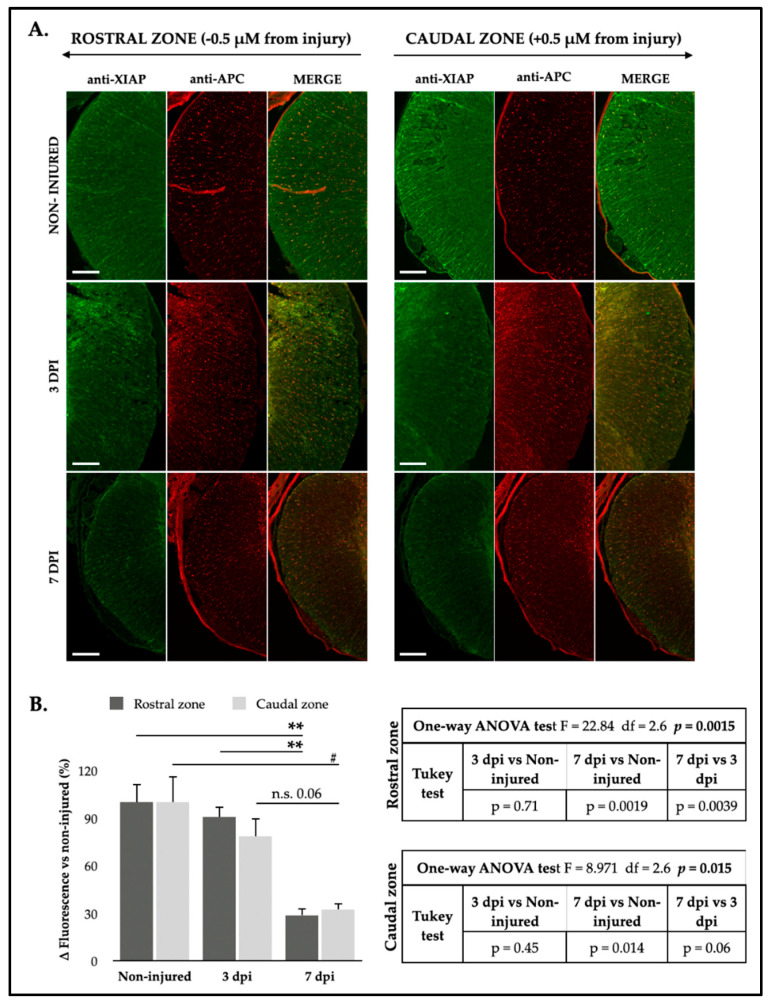
Figure 10.
Spinal cord injury causes a significant decrease in XIAP in oligodendrocytes. (A) Representative IF confocal images of rat spinal cords hemi-coronal sections of non-injured (upper row), 3 dpi (middle row), and 7 dpi (lower row), co-labeled with anti-XIAP antibody (green, left column) and anti-APC antibody (red, middle column) (n = 3 individuals per time). Sections are about 0.5 mm away from injury epicenter. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Analysis of XIAP staining intensity in rostral (dark gray bars) and caudal (light gray bars) spinal cord neurons in non-injured animals (0 dpi) and at 3 and 7 dpi. The graph represents the mean ± SD of sections from three animals per condition. Differences between conditions were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA test, followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test. ** denotes a significant difference (p < 0.01), # denotes a significant difference (p < 0.05), and n.s. denotes non significative respectively, relative to non-injured condition. For more detailed information on the analysis, please refer to the accompanying tables for the rostral zone (upper table) and the caudal zone (lower table).