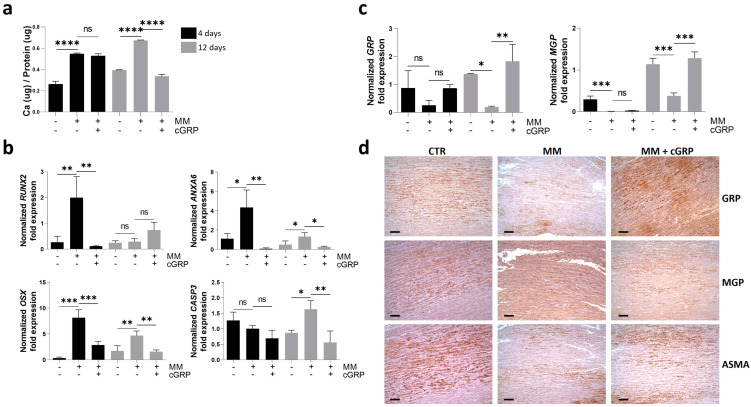
Figure 1.
γ-carboxylated GRP (cGRP) inhibits VSMC osteogenic differentiation in ex vivo aortic fragments by downregulation of osteogenic-related genes and upregulation of mineralization inhibitors. Aortic fragments were cultured under control, mineralization (MM), and MM supplemented with cGRP media conditions for 4 (black bars) and/or 12 days (grey bars). (a) Calcium (Ca) quantification normalized to total protein levels. (b) Relative gene expression by qPCR of the osteogenic markers runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), osterix (OSX), annexin A6 (ANXA6), and the apoptotic marker caspase 3 (CASP3). (c) Relative gene expression by qPCR of the mineralization inhibitors gla rich protein (GRP) and matrix gla protein (MGP). SD was calculated from 3 independent experiments (n = 3) and ANOVA, with comparison between groups by the Dunnett test, was performed relative to the MM condition. Statistical significance was defined as p ≤ 0.05 (*), p ≤ 0.01 (**), p ≤ 0.001 (***), and p ≤ 0.0001 (****); ns, non-significant. (d) Representative immunohistochemical (IHC) experiments in consecutive tissue sections of aortic fragments cultured for 12 days in control (CTR), MM, and MM supplemented with cGRP (MM + cGRP) conditions, to detect GRP, MGP, and α-smooth muscle actin (ASMA). Gamma adjustments were performed to homogenize the panel and were applied to the entire image. Scale bar, 100 μm.