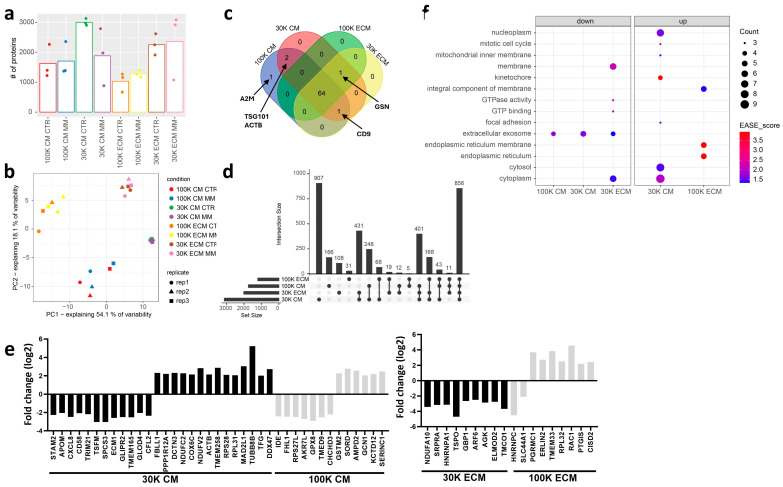
Figure 5.
Proteomic characterization of VSMC EVs. (a) Protein identification rates per experimental condition (i.e., each of the eight combinations of EV subpopulation and culture condition). (b) Principal component analysis scatter plot, showing sample projections on the first two principle components. (c) Venn diagram relating the four EV populations in terms of the fraction of their protein content belonging to Vesiclepedia’s top 100 most frequently detected proteins. (d) UpSet diagram for the full protein sets detected in the four EV populations. Each column on the x-axis refers to a subset of proteins from the universe of 3774 present in a defined combination of the four EV populations (black dots). (e) Log2 fold changes of proteins whose levels are altered (adj. p-value < 0.05 and |log2 fold change| >2) in MM relative to CTR condition in each of the four sample types. (f) Bubble plot showing enriched GO terms (EASE SCORE < 0.05) in the lists of upregulated and downregulated proteins from each sample type’s MM to CTR comparison. STAM2, signal transducing adapter molecule 2; APOM, apolipoprotein M; CXCL8, interleukin-8; CD58, lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3; TRIM21, E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21; TSFM, elongation factor Ts, mitochondrial; SPCS3, signal peptidase complex subunit 3; ECM1, extracellular matrix protein 1; GLIPR2, golgi-associated plant pathogenesis-related protein 1; TMEM165, transmembrane protein 165; GLOD4, glyoxalase domain-containing protein 4; CFL2, cofilin-2; FBLL1, rRNA/tRNA 2-O-methyltransferase fibrillarin-like protein 1; PPP1R12A, protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 12A; DCTN3, dynactin subunit 3; NDUFC2, NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 subunit C2; COX6C, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6C; NDUFV2, NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 2, mitochondrial; ACTB, actin, cytoplasmic 1; TMEM258, transmembrane protein 258; RPS28, 40S ribosomal protein S28; RPL31, 60S ribosomal protein L31; MAD2L1, mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2A; TUBB8B, tubulin beta-8 chain; TFG, protein TFG; DDX47, probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX47; IDE, insulin-degrading enzyme; FHL1, four-and-a-half LIM domains protein 1; RPS27L, 40S ribosomal protein S27-like; AKR7L, aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase member 4; GPX8, glutathione peroxidase 8; TMED9, transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 9; CHCHD3, MICOS complex subunit MIC19; GSTM2, glutathione S-transferase Mu 2; SORD, sorbitol dehydrogenase; AMPD2, AMP deaminase 2; GCN1, eIF-2-alpha kinase activator GCN1; KCTD12, BTB/POZ domain-containing protein KCTD12; SERINC1, serine incorporator 1; NDUFA10, NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 10, mitochondrial; SRPRA, signal recognition particle receptor subunit alpha; HNRNPA1, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1; TSPO, translocator protein; GBP1, guanylate-binding protein 1; ARF6, ADP-ribosylation factor 6; AGK, acylglycerol kinase, mitochondrial; ELMOD2, ELMO domain-containing protein 2; TMCO1, calcium load-activated calcium channel; HNRNPC, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins C1/C2; SLC44A1, choline transporter-like protein 1; PGRMC1, membrane-associated progesterone receptor component 1; ERLIN2, erlin-2; TMEM33, transmembrane protein 33; RPL32, 60S ribosomal protein L32; RAC1, ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; PTGIS, prostacyclin synthase; CISD2, CDGSH iron-sulfur domain-containing protein 2.