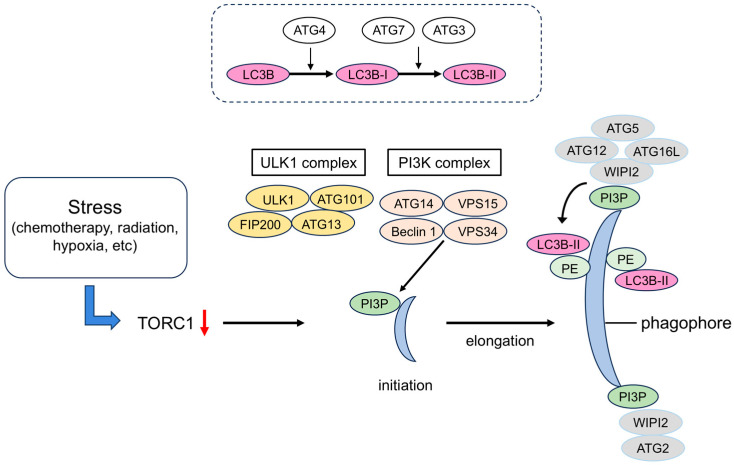
Figure 2.
Formation of autophagosomes. The ULK1 complex, which is involved in the initiation of autophagy, is inhibited by the mTORC1 kinase complex, so autophagy is induced when TORC1 is inactivated by factors such as nutrient starvation. When the ULK1 complex migrates to a subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the PI3K complex I is recruited, and the production of PI3P production increases. The PI3P-binding protein WIPI binds to it and accumulates at the site of autophagosome formation together with its partner ATG2. ATG2 anchors the ER and the phagophore and transports lipids. The ATG12 system is a system in which ATG12 and ATG5 are covalently bound to each other via a ubiquitin-like binding reaction. The ATG12–ATG5 complex forms a ternary complex with ATG16L and localizes to the phagophore, where it determines the location of amide bond formation between ATG8 family proteins (LC3B) and PE. LC3B-PE localizes to the inner and outer membranes of the phagophore and autophagosome, and it functions in membrane elongation and closure. TORC1, target of rapamycin complex 1; ULK1, Unc51-like kinase 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; PI3P, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate; WIPI, WD repeat domain phosphoinositide-interacting; ATG, autophagy-related protein; LC3B, light chain 3B; FIP200, focal adhesion kinase interacting protein; VPS34, vacuolar protein sorting 34.