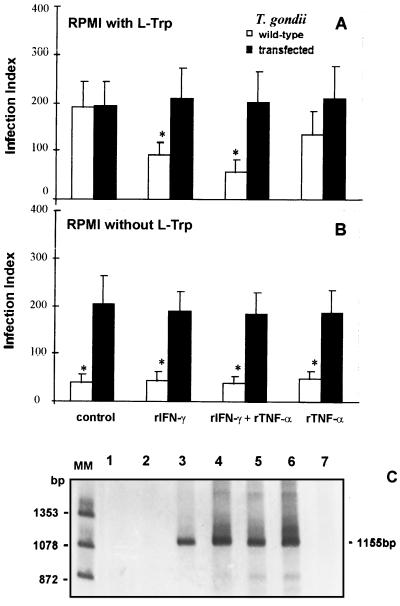
FIG. 4.
Comparison of effects of rIFN-γ (900 IU/ml) and/or rTNF-α (60 IU/ml) on 2C4 human fibroblasts infected with wild-type or transfected strains of T. gondii and maintained in the presence (A) or in the absence (B) of l-tryptophan (L-Trp). Both strains were maintained in tryptophan-free medium. RPMI was supplemented with 3% dialyzed heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum and 100 μM indole. The replication was evaluated 24 h after infection. An asterisk indicates a result statistically different from the control group (P < 0.05). Results indicate the means ± the standard errors of the means from three independent experiments done in duplicate. (C) PCR products of TS from E. coli. PCR was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The PCR product (3 μl) was electrophoresed in 6% polyacrylamide gel and silver stained. DNA of bacteriophage φX digested by endonuclease HaeIII was used as a molecular size marker. Lanes: 1 and 2, DNA from T. gondii RH wild-type strain, 1 and 10 ng, respectively; 3 and 4, T. gondii TS-transfected strain, 1 and 10 ng, respectively; 5 and 6, E. coli, 1 and 10 ng, respectively; 7, negative control (no DNA added). An 1,155-bp fragment was expected.