Fig. 1.
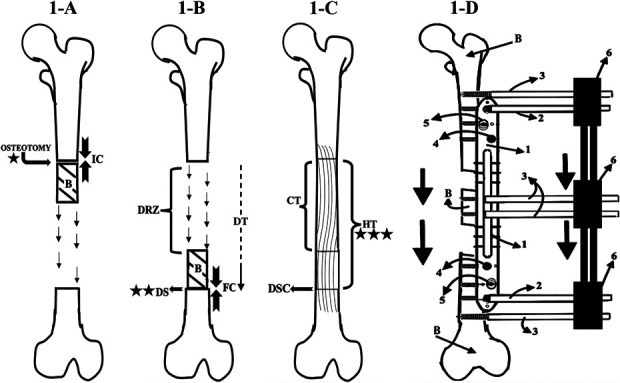
Figs. 1-A through 1-D Bone transport with an MIRP. Radiographic follow-up was first performed at the beginning of the latency phase (time 0; star), continued at the docking site during the distraction phase (2 stars) and the consolidation phase (allowing determination of the HT), and for an additional 6 months (3 stars). B = bone. Fig. 1-A Latency phase: This phase begins with osteotomy and measurement of the initial compression (IC), in Nm (defined as the torque resulting from a force of 1 Newton applied perpendicular to the end of a moment arm that is 1 meter long5,5). Its duration is the number of days for which the initial compression was applied. Fig. 1-B Distraction phase: At the end of this phase, the bone has been transported to the docking site (DS), and the measurement of the final compression (FC) in Nm is performed. The duration of this phase is the docking time (DT). DRZ = distraction regeneration zone. Fig. 1-C Consolidation phase. The duration of this phrase is the regenerate consolidation time (CT). The healing time (HT), from osteotomy to when consolidation of all bone has been completed, is the sum of the latency, distraction, and consolidation phases. Docking site consolidation = DSC. Fig. 1-D Diagram illustrating the bone transport process. 1 = rail plate, 2 = locking Schanz pin, 3 = simple Schanz pins, 4 = locking screw, 5 = conventional screw, and 6 = MEF (similar to the Orthofix product Monolateral External Fixator to Limb Reconstruction and Bone Elongation).
