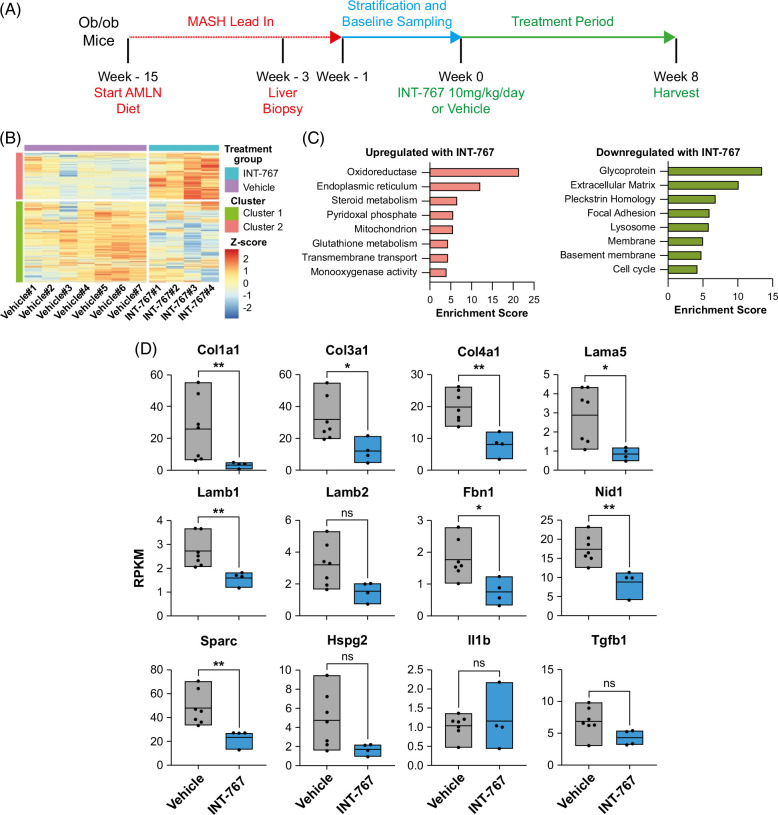
FIGURE 1.
INT-767 treatment inhibits basement membrane expression in AMLN ob/ob-MASH mice. (A) Summary of AMLN ob/ob-MASH mouse model. Lepob/ob mice on an AMLN diet for 12 weeks underwent liver biopsy. Mice with fibrosis stage ≥1 and steatosis score ≥2 continued the AMLN diet and were randomized to treatment with either INT-767 (10 mg/kg) or vehicle once daily for a further 8 weeks. (B) RNA-seq analysis of liver tissue demonstrates modules of differentially expressed genes that are downregulated (cluster 1) and upregulated (cluster 2) following INT-767 treatment. (C) Annotation of statistically significantly enriched functional categories of genes in cluster 1 and cluster 2 using the DAVID tool identifies the downregulation of extracellular matrix and basement membrane genes following INT-767 treatment. (D) Comparison of expression levels of stated gene between the vehicle (n = 7) and INT-767 (n = 4) treated mice using RNA-seq data. Levels of significance: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns p ≥ 0.05 (Mann-Whitney test). Abbreviations: AMLN, Amylin Liver NASH; MASH, metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis; RPKM, reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads.