Figure 2.
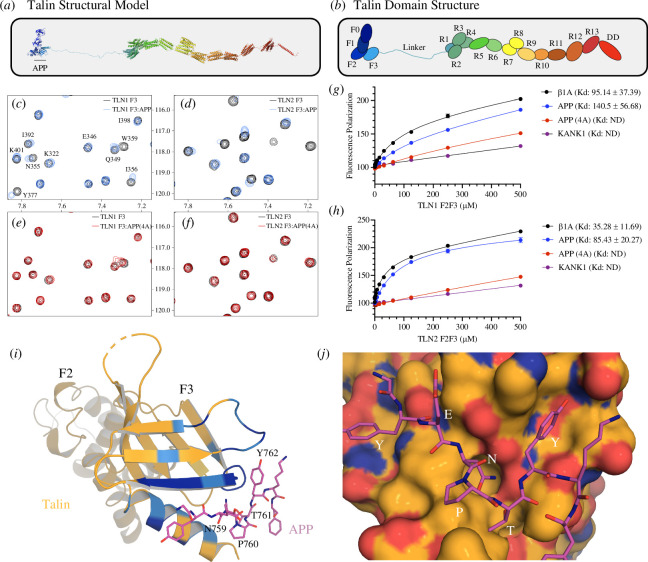
APP binds to talin directly. (a,b) Talin is a large, synaptic scaffold molecule comprised of an N-terminal FERM domain and a large rod domain comprised of 13 helical bundles, R1–R13, that act as force-dependent binary switches. The F3 domain is the NPxY motif binding domain. (c,d) 1H-15N HSQC spectra of 15N-labelled (c) talin1 F3 domain and (d) talin2 F3 domain in the absence (black) and presence of APP peptide (blue) at a ratio of 1 : 5. (e,f) 1H-15N HSQC spectra of 15N-labelled (f) talin1 F3 domain and (f) Talin2 F3 domain in the absence (black) and presence or APP(4A) peptide (red) at a ratio of 1 : 5. (g,h) A fluorescence polarization assay was used to determine the Kd of the interaction between integrin β1A, APP, APP (4A) and (g) talin1 and (h) talin2. Dissociation constants ± s.e. (µM) for the interactions are indicated in the legend. All measurements were performed in triplicate. ND, not determined. (i) The talin1/APP crystal structure. One heterodimer from the crystal structure of talin1 F2F3 bound to the APP cytoplasmic tail. The NPxY residues are labelled, and the colour coding is the chemical shift mapping from the NMR data in (c). (j) Surface representation of F3 coloured by electrostatics (red acidic, blue basic), showing the 757YENPTY762 motif bound. APP residues N759, T761 and Y762 fit into pockets on F3.