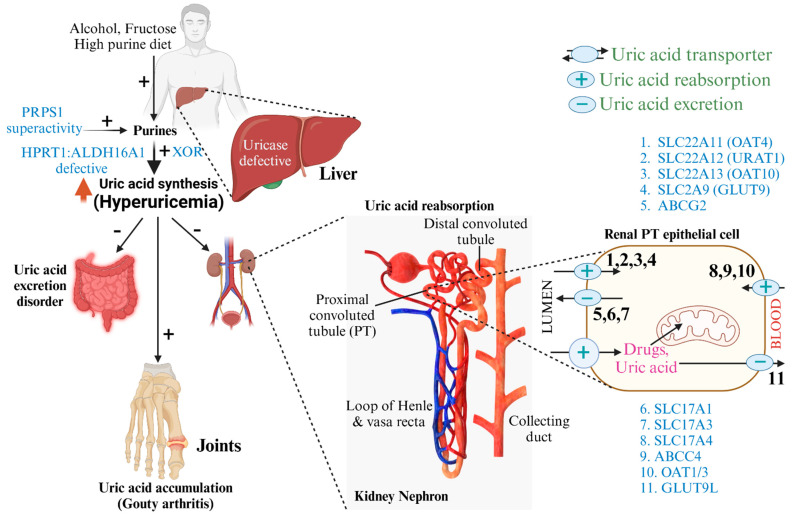
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of uric acid production and excretion: Illustrates the biochemical pathways involved in uric acid metabolism, highlighting key enzymes and intermediates. Xanthine oxidase (XO) or XOR catalyzes the conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine and, subsequently, to uric acid. Medications like allopurinol and febuxostat, XO inhibitors, reduce uric acid synthesis by inhibiting this enzyme, while rasburicase, a uricase analog, aids in uric acid breakdown. ALDH16A1 is a non-catalytic enzyme that causes gout via protein-protein interactions with HPRT1. OAT1/3 is situated on the basolateral membrane [29].