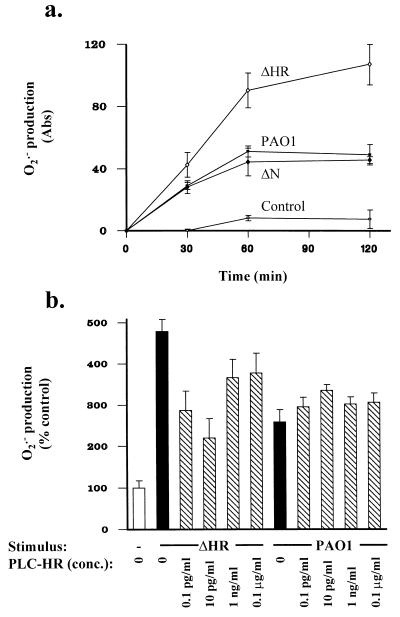
FIG. 1.
(a) Respiratory burst by neutrophils exposed to intact P. aeruginosa, as measured by cytochrome c reduction. Neutrophils had increased O2·− production when exposed to the ΔHR strain at 30 min (P < 0.05), 60 min (P < 0.001), and 120 min, compared to wild-type bacteria (PAO1). O2·− production induced by the ΔN strain was not different (P > 0.05) from that following exposure to wild-type bacteria. Neutrophils exposed to all bacterial strains produced greater O2·− levels than unstimulated neutrophils (P < 0.001). Abs, absorbance. (b) Neutrophils were pretreated with PlcHR (0.1 pg/ml to 0.1 μg/ml) for 15 min prior to addition of bacteria. Addition of ΔHR or PAO1 increased O2·− production by neutrophils (P < 0.01). PlcHR decreased (P < 0.05) O2·− production stimulated by ΔHR but not that by wild-type bacteria.