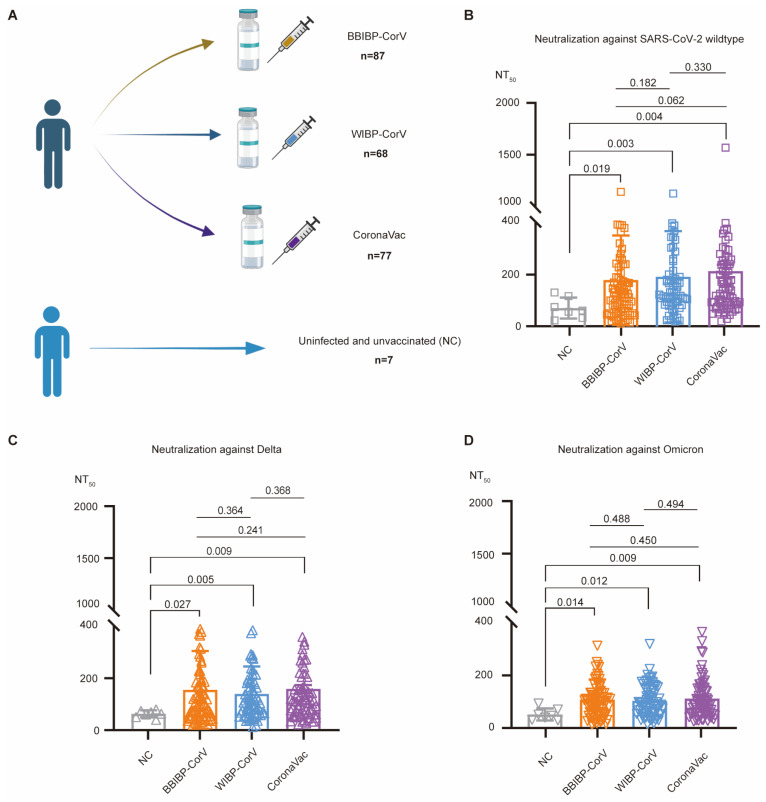
Figure 1.
Three distinct types of inactivated vaccines elicited significantly higher levels of serum neutralization against wildtype SARS-CoV-2, Delta, and Omicron (B.1.1.529). (A) Recruitment of donors. In total, 239 volunteers were selected for this study, including 87 BBIBP-CorV vaccinees, 68 WIBP-CorV vaccinees, 77 CoronaVac vaccinees, and 7 uninfected, unvaccinated, negative-control (NC) donors. (B–D) Comparison of serum neutralizing titers against wildtype SARS-CoV-2 (square, B), Delta (up-pointing triangle, C), and Omicron (B.1.1.529) (down-pointing triangle, D). In each graph, each dot represents a donor, with his/her serum neutralizing titer (NT50 values on the y-axis) calculated based on in vitro neutralization assays. Donors receiving distinct types of inactivated vaccines are shown on the x-axis and represented by different colors: gray, uninfected unvaccinated donors as negative controls (NC); orange, BBIBP-CorV-vaccinated donors; blue, WIBP-CorV-vaccinated donors; and purple, CoronaVac-vaccinated donors. The serum neutralizing activity (NT50) of these four groups of donors were compared with each other using Kruskal–Wallis test, with the calculated p-values shown above the column.